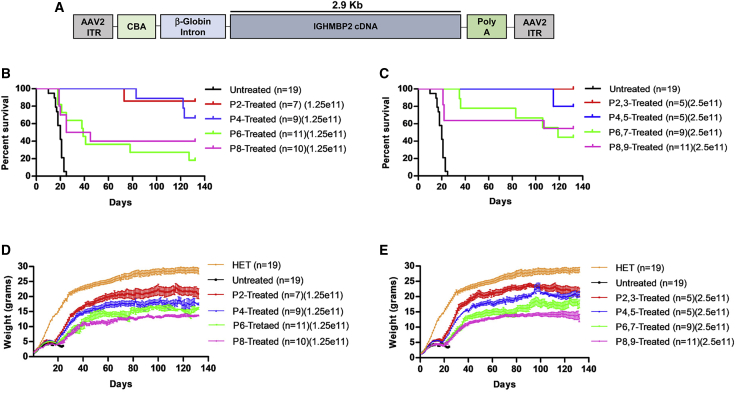
Figure 1.
ICV injection of AAV9-IGHMBP2 in low and high dose significantly increases the survival and weight of FVB-nmd at early and late time points
(A) Map of AAV9-IGHMBP2 containing 2.9 kb of human IGHMBP2 cDNA under control of the ubiquitously expressing chicken-beta-actin (CBA) promoter. (B and C) Homozygous FVB-nmd mice were i.c.v. injected at P2, P4, P6, and P8, using a low dose (1.25 × 1011 vg) (B) and at P2,3, P4,5, P6,7, and P8,9 using a high dose (2.5 × 1011 vg) (C) of AAV9-IGHMBP2 and compared to untreated mice. Survival was determined by Kaplan-Meier curves, and p value was calculated by the log-rank (Mantel-Cox) test. Median survival of either low- or high-dose treated at P2 and P4 were undefined, since most of the animals in each group were alive at day 132, living significantly longer than untreated mice, which had a median survival of 20 days (p < 0.0001) (B and C). Low-dose P6- and P8-treated FVB-nmd mice had a median survival of 39 and 35 days, respectively (p = 0.48), which was significantly longer than untreated (P6 versus untreated, p = 0.0002; P8 versus untreated, p = 0.001) (B). The median survival of high-dose-treated mice at P6 and P8 was 119 days and undefined, respectively (P6,7 and P8,9 versus untreated, p < 0.0001) (C). (D and E) Weight gain of low- (D) and high-dose-treated (E) mice at P2, P4, P6, and P8 is assessed and compared to untreated. The average weight of both low- (D) and high-dose-treated (E) animals at every time point was significantly higher than untreated FVB-nmd mice, which weigh 3.6 ± 0.18 g (one-way ANOVA p < 0.0001). The average weight of both low- and high-dose-treated animals was significantly different between each group based on the time point of therapy. P2-treated mice weighing 17.39 ± 0.53 in low dose and 18.22 ± 0.58 g in high dose were significantly heavier than P4 mice, which weighed 14.41 ± 0.44 in low-dose and 16.06 ± 0.51 g in high-dose groups (one-way ANOVA, p < 0.001 for low dose; p < 0.01 for high dose). P4 weight was significantly higher than P6, weighing an average of 12.18 ± 0.39 in low-dose-treated mice and 13.14 ± 0.43 g in high-dose-treated mice (one-way ANOVA, p < 0.01 for low dose; p < 0.001 for high dose). P6 was drastically heavier than P8, with average weight of 10.45 ± 0.32 in low-dose-treated and 11.21 ± 0.34 g in high-dose-treated mice (one-way ANOVA, p < 0.05 for low dose; p < 0.01 for high dose). Error bars represent ± SEM.