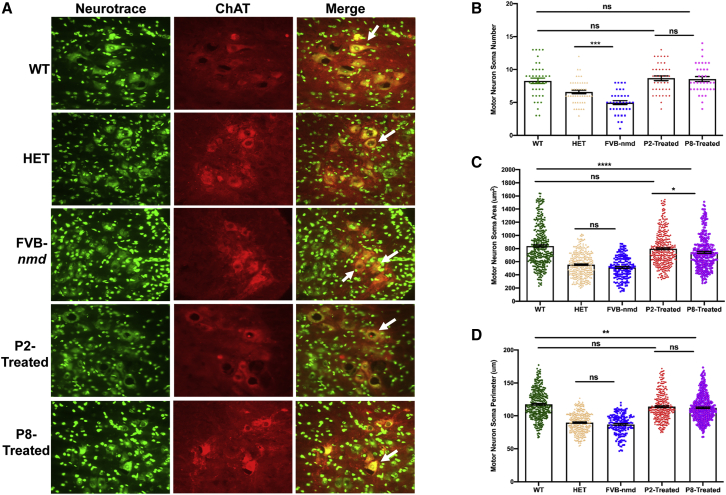
Figure 5.
I.c.v. delivery of AAV9-IGHMBP2 in high dose improved the motor neuron number and area size in the lumbar region of FVB-nmd mice at early and late time points
(A) Nissl body (NeuroTrace) and anti-choline acetyl transferase (ChAT) were used to immunostain motor neurons from cross-sections of lumbar spinal cord (L3–L5). High-dose P2- and P8-treated mice (n = 4) were compared to age-matched WT littermates (P42) (n = 3), while untreated FVB-nmd mice (n = 4) were evaluated in comparison to the age-matched HET mice (P14) (n = 3). Fluorescent representative images were taken at 40× magnification. (B) The number of motor neurons in FVB-nmd mice was drastically less than HET (one-way ANOVA, p < 0.001), while the motor neuron numbers in P2 and P8 were similar to the WT cohort (p > 0.5). (C and D) The area and perimeter of the motor neurons in FVB-nmd mice was not statistically different from HET (p > 0.5). P2- and P8-treated motor neurons were smaller than WT in area and perimeter with varying degrees (one-way ANOVA, P2 versus WT, p < 0.05; P8 versus WT, p < 0.001). P2-treated and P8-treated mice differed only in the area of the motor neuron soma (p < 0.05) (C and D). Scale bar, 50 μm. Error bars represent mean ± SEM.