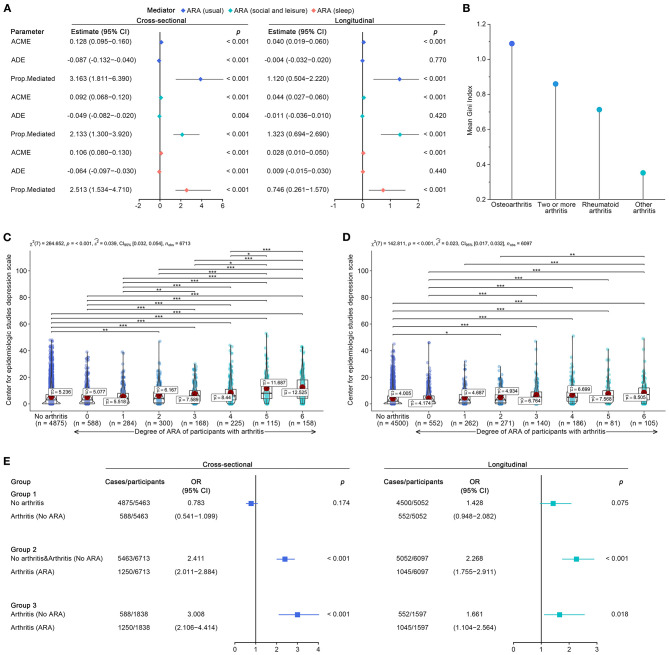
Figure 2.
Further analyses for restriction of activities, and subtypes in arthritis. (A) Results of cross-sectional and longitudinal mediation analysis for arthritis, in which ARA (usual), ARA (social and leisure), and ARA (sleep) were considered as potential mediators. (B) Random-Forest algorithm-derived Mean Gini Index weighed the contribution of arthritis subtypes to outcomes of depression. (C) Cross-sectional potential difference of depressive symptoms among participants with/without arthritis (stratified by degree of ARA). (D) Longitudinal potential difference of depressive symptoms among participants with/without arthritis (stratified by degree of ARA). (E) Stratified analyses using binomial logistic regression quantified associations between arthritis (No ARA), arthritis (ARA), and depression at baseline and Wave 2. ARA, Restriction of activities caused by arthritis; ACME, average causal mediation effects; ADE, average direct effects; Prop. mediated, proportion mediated; χ2, chi-square; nobs, number of observation; û, group mean; effect size of ε2; p, p-value. p-value adjusted < 0.05 was represented by “*,” p-value adjusted < 0.01 was represented by “**,” p-value adjusted < 0.001 was represented by “***”.