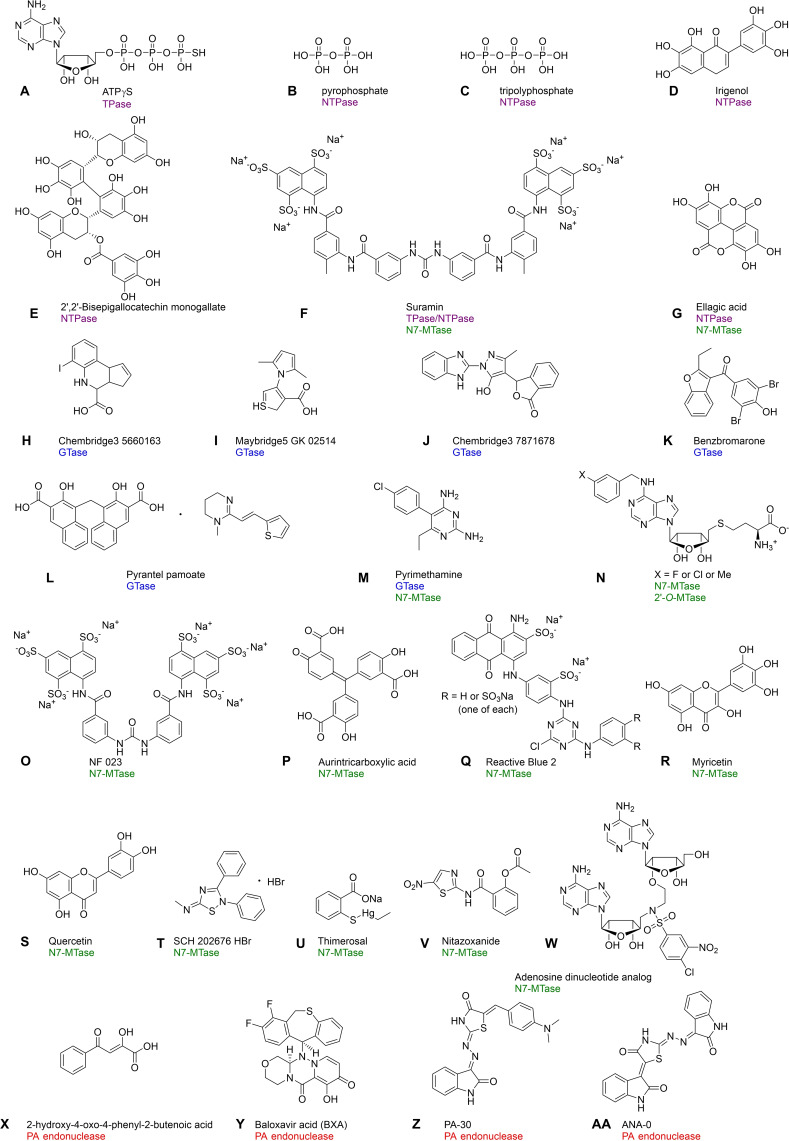
Figure 8.
Structures of RNA‐capping inhibitors identified by assays dedicated for monitoring the activity of enzymes involved in cap biosynthesis: A) ATPγS; [71] B) Pyrophosphate; [77] C) Tripolyphosphate; [77] D) Irigenol;[ 81 , 82 ] E) 2′,2′‐Bisepigallocatechin monogallate;[ 81 , 82 ] F) Suramin;[ 74 , 133 ] G) Ellagic acid;[ 81 , 82 , 115 ] H) Chembridge3 5660163; [103] I) Maybridge5 GK 02514; [103] J) Chembridge3 7871678; [103] K) Benzbromarone; [104] L) Pyrantel pamoate; [104] M) Pyrimethamine; [106] N) (3‐Fluorobenzyl)‐N6‐SAH (X=F), (3‐chlorobenzyl)‐N6‐SAH (X=Cl) and (3‐methylbenzyl)‐N6‐SAH (X=CH3); [122] O) NF 023; [133] P) Aurintricarboxylic acid; [133] Q) Reactive Blue 2; [133] R) Myricetin;[ 115 , 133 , 134 ] S) Quercetin;[ 115 , 133 , 134 ] T) SCH 202676 HBr; [134] U) Thimerosal; [134] V) Nitazoxanide; [131] W) Adenosine dinucleotide/SAM analogue (bisubstrate inhibitor); [145] X) 2‐Hydroxy‐4‐oxo‐4‐phenyl‐2‐butenoic acid; [137] Y) Baloxavir acid (BXA); [138] Z) P‐30; [67] and AA) PA‐48. [67]