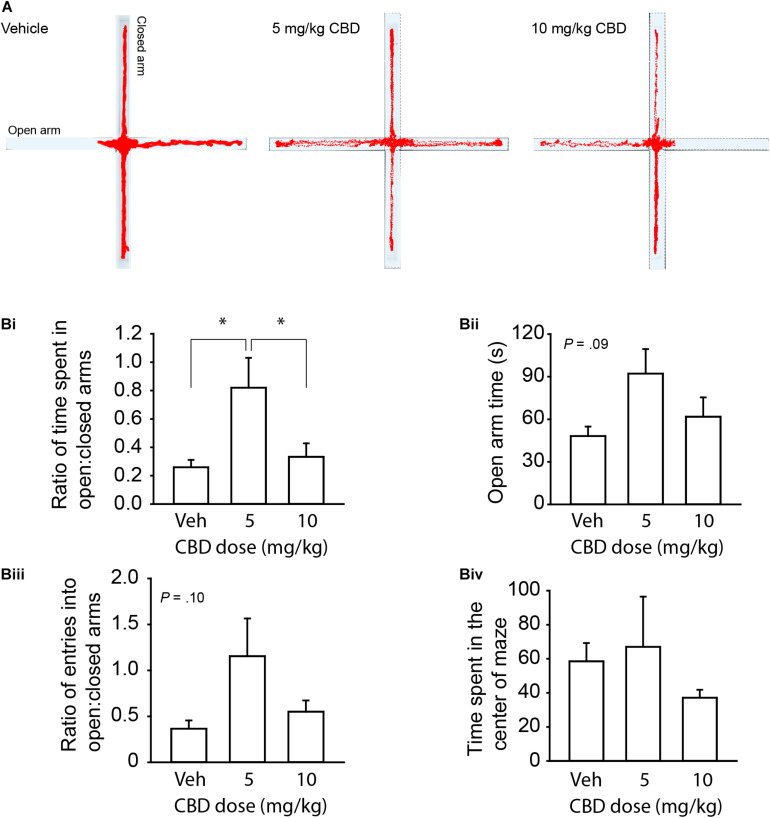
FIGURE 1.
CBD dose dependently reduces anxiety-like behavior on the EPM in adult mice. (A) Representative activity traces of subjects administered vehicle, 5 mg/kg CBD, and 10 mg/kg CBD. (Bi) Summary bar chart showing that 5 mg/kg CBD increased the ratio (left) of time spent in the open arm relative to the closed arm (0.82 ± 0.21, n = 6) compared to vehicle (0.26 ± 0.05, n = 6) and 10 mg/kg (0.33 ± 0.10, n = 6) treated mice. (Bii) Summary bar chart showing the trend (P = 0.09) for CBD to affect time spent in the open arms by one-way ANOVA. 5 mg/kg treated mice spent more time in the open arm (92.10 ± 17.31 s) compared to vehicle (48.00 ± 6.78 s) and 10 mg/kg (61.8 ± 13.68 s) treated mice. (Biii) Summary bar chart showing a trend (P = 0.10) for CBD to affect the ratio of entries into the open:closed arms of the EPM by one-way ANOVA. 5 mg/kg treated mice had a higher ratio of entries into the open arms compared to the closed arms (1.16 ± 0.41) compared to vehicle (0.37 ± 0.09) and 10 mg/kg (0.55 ± 0.12) treated mice. (Biv) Summary bar chart showing that there were no differences between treatment groups in time spent in the center square of the EPM. ∗indicates P < 0.05 by Tukey’s HSD post hoc comparisons.