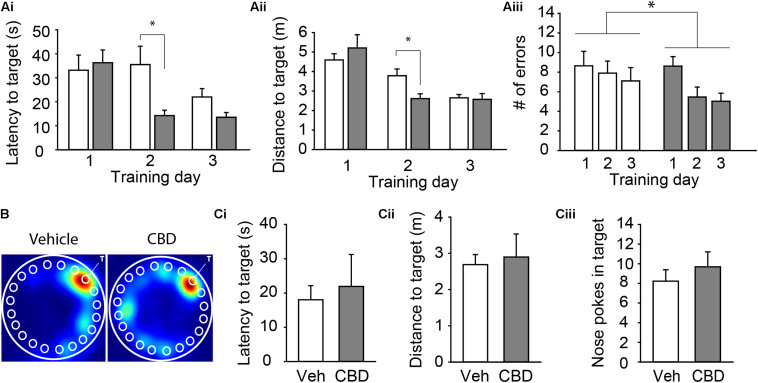
FIGURE 3.
Adolescent CBD exposure improves the rate of learning of a spatial memory task. Summary bar charts showing the mean latency (Ai) and mean distance traveled (Aii) to the escape box as well as the mean number of errors (Aiii) on each day of acquisition. CBD-treated mice had shorter latency to target (14.29 ± 4.85 s) and distance to target (2.61 ± 0.38 m) on day 2 compared to vehicle treated mice (38.09 ± 5.05 s; 3.78 ± 0.39 m). CBD treated mice made fewer errors across all acquisition days (6.37 ± 0.59 errors) than vehicle-treated mice (7.88 ± 0.77 errors). (B) Representative heat maps in the Barnes maze on the probe day of subjects administered vehicle (left) and CBD (right). The white “T” indicates target hole. Summary bar charts showing that there was no difference in the latency to the target hole (Ci), distance to the target hole (Cii), or number of nose pokes into the target hole (Ciii) on the probe day between the vehicle (18.04 ± 4.12 s; 2.69 ± 0.28 m; 8.23 ± 1.16 nose pokes) and CBD (21.93 ± 0.93 s; 2.90 ± 0.64 m; 9.69 ± 1.52 nose pokes) treated groups. ∗indicates P < 0.05 by Tukey’s HSD post hoc comparisons.