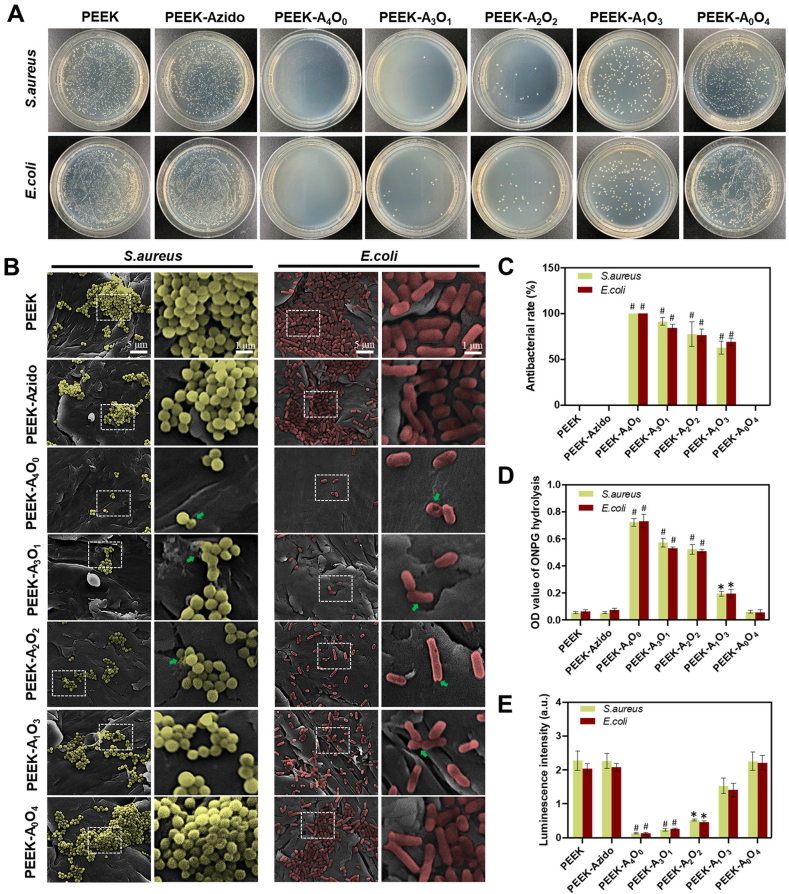
Fig. 4.
In vitro antibacterial activity. (A) Solid culture after incubating E. coli and S. aureus (107 per mL) on different samples for 12 hours. (B) FE-SEM images of S. aureus and E. coli cultured on different surfaces (scale bar = 5 μm and 1 μm, respectively). S. aureus was labelled with yellow color and E. coli was red. The damages of cell walls were marked by green arrows. (C) Antibacterial activity of different groups determined by counting the bacterial colonies (n = 4 per group). (D) The results of ONPG hydrolysis assay (n = 4 per group). (E) The results of ATP test (n = 4 per group). Statistically significant differences were indicated by *p < 0.05 and #p < 0.01 compared with the bare PEEK group.