Figure 1.
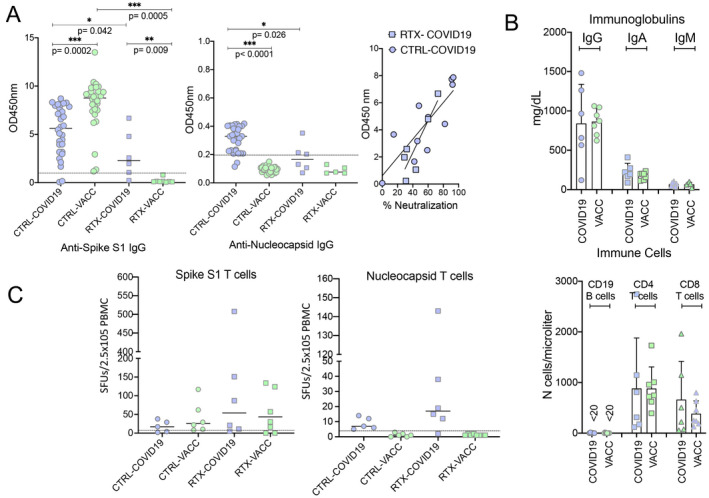
Anti‐SARS–CoV‐2 immune responses in previously infected patients and vaccinated patients who have undergone B cell depletion. A, Antibodies against the spike S1 protein of SARS–CoV‐2 (assessed by enzyme‐linked immunosorbent assay [ELISA]; Euroimmun) (left) and nucleocapsid protein of SARS–CoV‐2 (assessed by ELISA; Epitope) (middle), and correlation between neutralizing antibody activity (percent inhibition of binding of spike S1 protein–expressing cells to angiotensin‐converting enzyme 2) and the spike S1 protein antibody response (OD at 450 nm) (right). Tests were performed in 30 healthy controls after SARS–CoV‐2 infection (CTRL‐COVID‐19), 30 healthy controls after SARS–CoV‐2 mRNA vaccination (CTRL‐VACC), 6 rituximab‐treated, B cell–depleted autoimmune disease patients after SARS–CoV‐2 infection (RTX‐COVID19), and 8 rituximab‐treated, B cell–depleted autoimmune disease patients after SARS–CoV‐2 mRNA vaccination (RTX‐VACC). Symbols represent individual subjects; horizontal lines show the mean. Comparisons were conducted using Wilcoxon’s signed rank sum test. B, Serum levels of IgG, IgA, and IgM (top) and numbers of CD19 B cells, CD4 T cells, and CD8 T cells (bottom) in rituximab‐treated, B cell–depleted autoimmune disease patients after SARS–CoV‐2 infection and rituximab‐treated, B cell–depleted autoimmune disease patients after SARS–CoV‐2 mRNA vaccination. Symbols represent individual subjects; bars show the mean ± SD. C, Enzyme‐linked immunospot assay results showing T cell responses to antibodies against the spike S1 protein (left) and the nucleocapsid protein (right) in healthy controls after SARS–CoV‐2 infection, healthy controls after SARS–CoV‐2 mRNA vaccination, rituximab‐treated B cell–depleted autoimmune disease patients after SARS–CoV‐2 infection, and rituximab‐treated, B cell–depleted autoimmune disease patients after SARS–CoV‐2 mRNA vaccination. Symbols represent individual subjects; horizontal lines show the mean. SFUs = spot‐forming units; PBMC = peripheral blood mononuclear cell.
