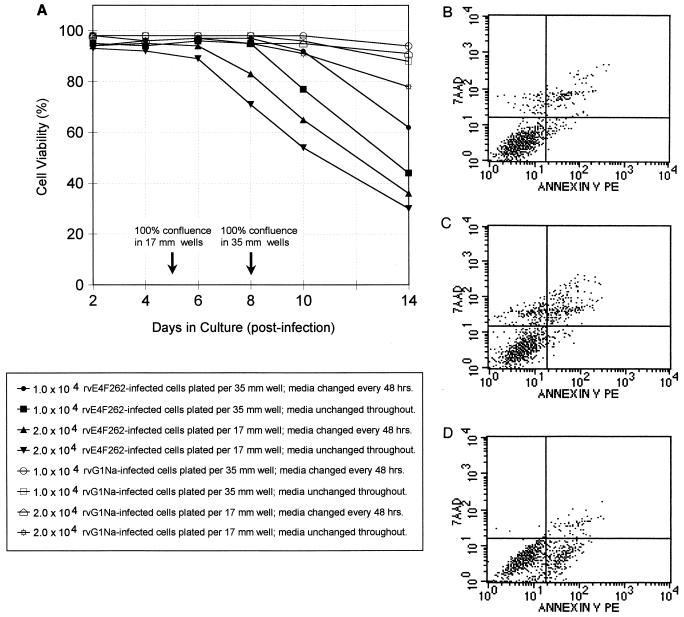
FIG. 6.
Culture conditions influence the onset and mechanism of cell death in rvE4F262-infected E1A13S/ras cells. (A) Quadruplicate cultures of rvE4F262- or rvG1Na-infected E1A13S/ras cells were replated at two cell densities, 104 cells/35-mm-diameter well and 2.0 × 104 cells/17-mm-diameter well. Half of each set of cultures received fresh medium every 48 h; the medium was unchanged in the other half. Average cell viability from duplicate wells was determined by trypan blue exclusion at the indicated times; standard deviations were ≤10% between duplicates at all points. Two independent experiments were performed, and the results from one representative experiment are shown. (B to D) Quadruplicate sets of rvE4F262-infected E1A13S/ras cells were replated at 2.0 × 104 cell/17-mm-diameter well with fresh medium every 48 h (B), 104 cells/35-mm-diameter well with no fresh media after plating (C) and 104 cells/35-mm-diameter well with fresh medium every 24 h (D). Cells were stained with annexin V-PE and 7-AAD and analyzed by FACS approximately 48 h after reaching confluence. Representative histograms from each quadruplicate set are shown. Viable cells not undergoing cell death do not bind annexin V and exclude 7-AAD (lower left quadrant); cells in early apoptosis bind annexin V but still exclude 7-AAD (lower right quadrant); cells in early necrosis do not bind annexin V but do not exclude 7-AAD (upper right quadrant); cells in late apoptosis or necrosis and dead cells bind annexin V and do not exclude 7-AAD (upper right quadrant). Quadrant boundaries were set by using rvG1Na-infected E1A13S/ras cells and uninfected NIH 3T3 cells.