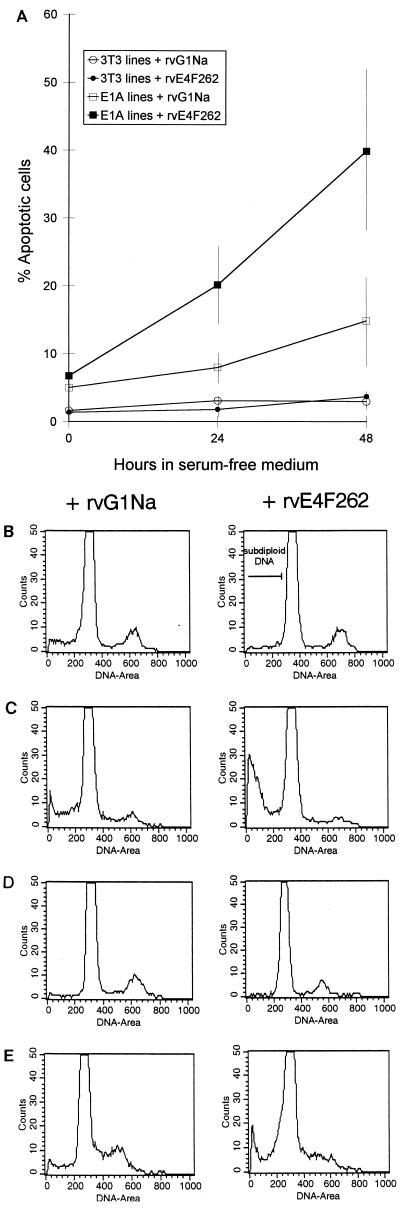
FIG. 7.
E4F262 expression increases E1A-induced apoptosis in serum starved NIH 3T3 cells. After infection by rvE4F262 or control virus (rvG1Na), two independent E1A12S/3T3 cell lines, one E1A13S/ras cell line, one 3T3/ras cell line, and parental NIH 3T3 cells were replated at 104 cells/ 35-mm-diameter well, cultured for 48 h, and then shifted to serum-free medium for 24 and 48 h. At each time point, the degree of apoptosis was determined by the percentage of cells with a subdiploid DNA content as measured by PI-FACS analysis. (A) Average percentages of apoptotic cells from E1A-expressing and non-E1A-expressing (3T3) cell lines infected with rvE4F262 or rvG1Na. Standard deviations are indicated by thin vertical lines. (B to E) Representative DNA histograms of rvE4F262- or rvG1Na-infected NIH 3T3 (B), E1A12S/3T3 (C), 3T3/ras (D), and E1A13S/ras (E) cells after 24 h in serum-free medium. The position of the subdiploid DNA peak is indicated by a bar in the upper right panel.