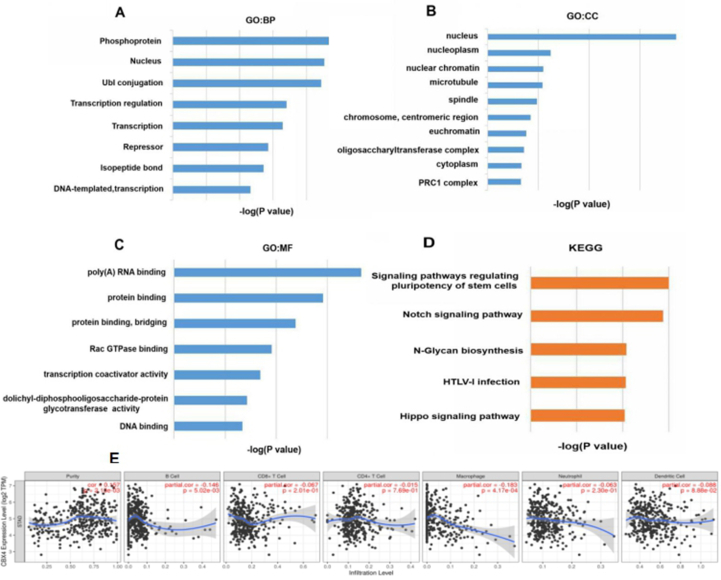
Figure 7.
Predicted functions and pathways enriched in CBX4 and its 100 most frequently altered neighboring genes in GC patients (DAVID 6.8) and immune cell infiltration of CBX4 in GC patients (TIMER). (A) Among the 10 most highly enriched functions in the BP category, the phosphoprotein, nucleus, Ubl conjugation, transcription regulation and transcription BPs were remarkably enriched in CBX4 in GC. (B) PRC1 complex, cytoplasm, oligosaccharyl transferase complex, euchromatin chromosome, centromeric region, spindle, microtubule, nuclear chromatin, nucleoplasm, and nucleus were the ten CCs most highly enriched in CBX4. (C) Among MFs, CBX4 and its neighboring genes were mainly enriched in poly(A) RNA binding and protein binding. (D) As for KEGG pathway analysis, the following 5 pathways were significantly enriched in CBX4 in GC: the stem cell pluripotency signaling pathway, Hippo signaling pathway, HTLV-I infection pathway, Notch signaling pathway, and N-glycan biosynthesis pathway. (E) CBX4 expression was negatively associated with the infiltration of B cells and macrophages.