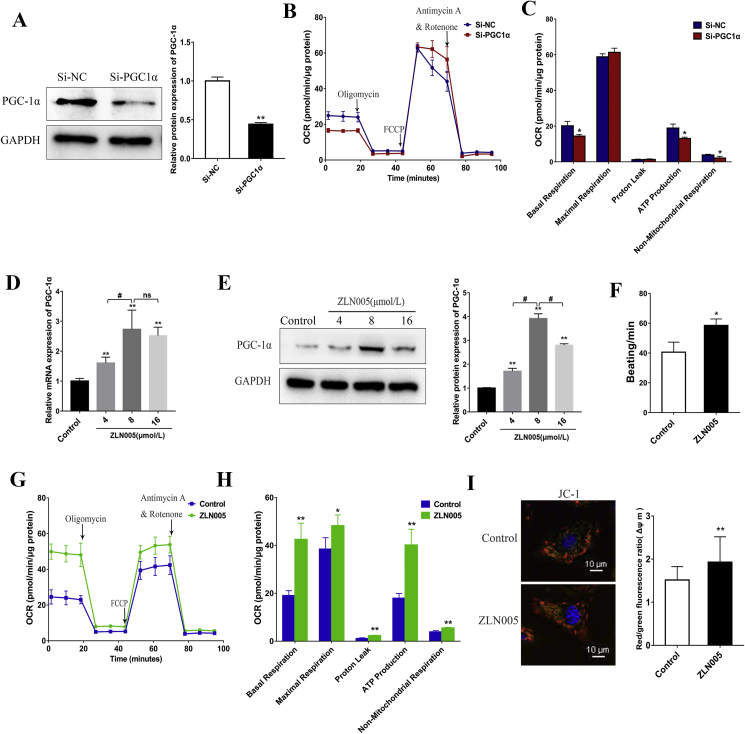
Figure 3.
PGC-1α plays an important role in cardiomyocyte mitochondrial respiratory function. (A) Western blot analysis detected the expression of PGC1α in hiPSC-CMs treated with negative control siRNA (Si-NC) or PGC-1α siRNA (Si-PGC1α). (B) Representative two OCR traces of hiPSC-CMs treated with negative control siRNA (Si-NC) or PGC-1α siRNA (Si-PGC1α) for 3 days, respectively, in response to oligomycin, FCCP, and antimycin A. (C) OCR parameters representing mitochondrial function in PGC-1α siRNA-treated hiPSC-CMs were significantly reduced. (D–E) RT-qPCR (D) and Western blot analysis (E) of PGC-1α expression in hiPSC-CMs treated with ZLN005 at different concentrations (0, 4, 8, 16 μmol/L). 8 μmol/L ZLN005 could effectively upregulate the expression of PGC-1α. (F) Upregulating PGC-1α by ZLN005 (8 μmol/L) increased beating frequency of hiPSC-CMs. (G) Representative traces for control and 8 μmol/L ZLN005-treated hiPSC-CMs responding to oligomycin, FCCP, and rotenone and antimycin A. (H) OCR parameters representing mitochondrial function in 8 μmol/L ZLN005-treated hiPSC-CMs were significantly increased. (I) Mitochondrial membrane potential analysis was measured using a fluorescence probe JC-1 assay system in day 0-hiPSCs and day 30-hiPSC-CMs. The ratio of red/green fluorescence represented the level of Δψm. Compared with control group, ∗P < 0.05, ∗∗P < 0.01; ns, no significant difference.