FIGURE 1.
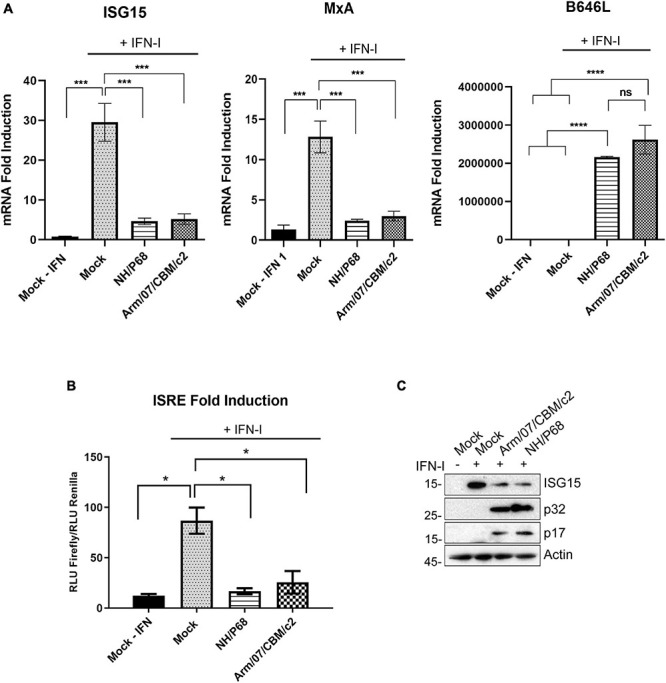
NH/P68 and Arm/07/CBM/c2 ASFV strains are able to impair IFN-I signaling. PAMs were either mock infected or infected with NH/P68 or Arm/07/CBM/c2 ASFV strains (1 PFU/cell). At 16 h post-infection, cells were mock treated or treated with universal type I IFN (1,000 U/ml) for 8 h. ISG15 and MxA mRNAs were measured by qRT-PCR (A). As a control of infection, ASFV viral B646L gene mRNA was determined. The obtained values were relativized against the mock infected and untreated sample. All data are means ± SEM (n = 3). One-way ANOVA statistical analysis and Tukey’s multiple comparison test were performed (*p < 0.05, ***p < 0,001; ****p < 0,0001). ISRE-luciferase reporter assay in mock infected or infected COS-1 cells with either NH/P68 or Arm/07/CBM/c2 strains (1 PFU/cell, 16hpi) treated or not with type I IFN (1,000 U/ml) (B). Graphs represent the means of the Firefly luciferase RLU (Relative Luminiscence Units) values divided by its Renilla luciferase RLU values from biological triplicates. The obtained values were relativized against the mock infected and untreated sample. Two-tailed t-test comparison made with Mock + IFN (*p < 0.05). Western blot analysis of ISG15, viral p17, p32 and actin expression in COS-1 cells lysates previously used for the luciferase assay (C).
