Figure 3. Proposed mechanisms of NAPQI formation.
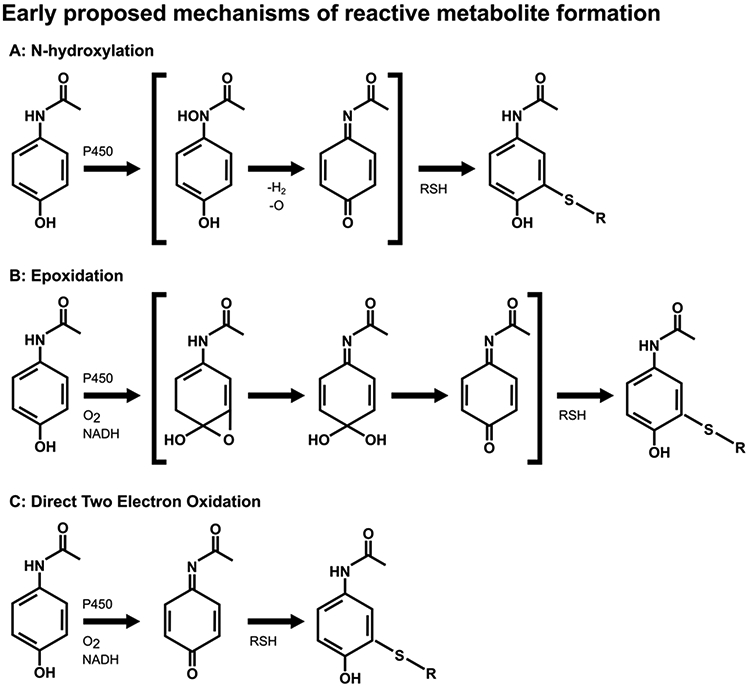
Initially, it was thought that formation of the reactive metabolite of APAP may precede through N-hydroxylation (A) or epoxidation (B), as shown. These mechanisms were proven to be incorrect. (C) It is now thought that APAP is directly oxidized by a two-electron oxidation, a previously unrecognized cytochrome P-450 mechanism. Once formed, NAPQI readily reacts with sulfhydryl groups, such as on GSH or cysteine residues in proteins.
