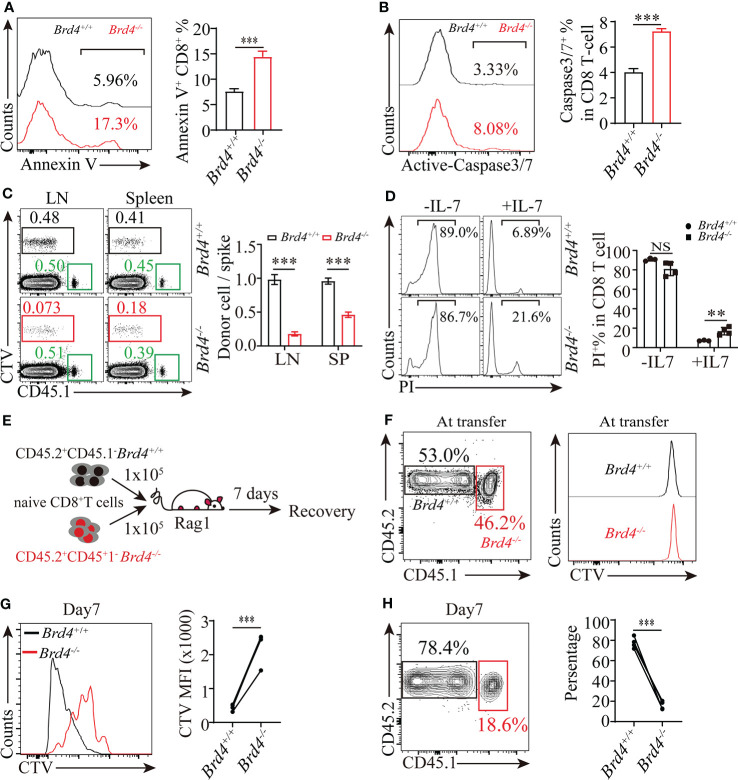
Figure 2.
Brd4 is essential for naïve CD8+ T cells survival and homeostasis proliferation. (A) Flow cytometry showing the frequency (left) and quantification (right) of Annexin-V+ CD8+ T cells. (B) Flow cytometry showing the frequency (left) and quantification of active-caspase3/7+CD8+ T cells (right). (C) Purified Brd4+/+ and Brd4 -/- naïve CD45.2+CD8+ T cells were labeled with CellTrace Violet (CTV) and respectively transferred with naïve CD45.1+CD8+ T cells (spike) into CD45.2+ recipient mice to monitor the survival capability of naïve CD8+ T cells for 7 days in vivo. Flow analysis of donor naïve CD8+ T cells in spleen and lymph node at day 7 post-transfer (left) and the relative ratio of recovered donor cells to spike (right). (D) Sorted naïve CD8+ T cells from Brd4-/- and Brd4+/+ mice were cultured with or without IL-7 for 3 days to test IL-7 triggered survival effect. (E) Experimental setup. Congenically marked Brd4+/+ and Brd4 -/- naïve CD8+ T cells were labeled with CTV, mixed at a 1:1 ratio, and then transferred into Rag1 mice to monitor cell proliferation at day 7 post-transfer. (F) Relative frequency of donor cells at transfer. (G) Representative flow analysis of donor cells recovered at day 7 post-transfer. (H) The quantification of donor CD8+ T cells at day 7 post transfer. Two-tailed unpaired t-test was used to analyze two independent groups, while paired Student’s t-test was used when sample being compared from same mouse. Results were indicated as mean ± sem (error bars). **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001. NS, not significant. Each group includes at least 3 mice and each experiment repeats more than 3 times.