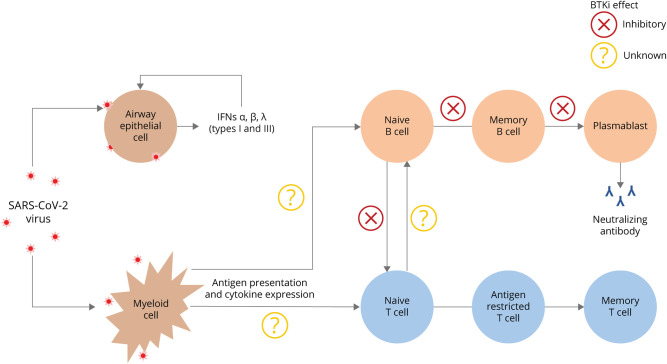
Figure 1. Theoretical Effects of BTKis on Immune Response to SARS-CoV-2 Infection or Vaccines.
Early SARS-CoV-2 infection predominantly targets airway epithelial cells. Myeloid cells, including antigen-presenting cells, respond early in the course of infection, conditioning downstream responses of lymphocytes. Inhibition of BTK may affect multiple points of the immune response. BTKis prevent the development of naive B cells to memory B cells or plasmablasts, which are required for antibody generation. Antigen presentation and cytokine signaling among myeloid cells, B cells, and T cells may be altered or inhibited by BTK. BTK = Bruton tyrosine kinase; BTKi = Bruton tyrosine kinase inhibitor; IFN = interferon; SARS-CoV-2 = severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2.