Figure 3.
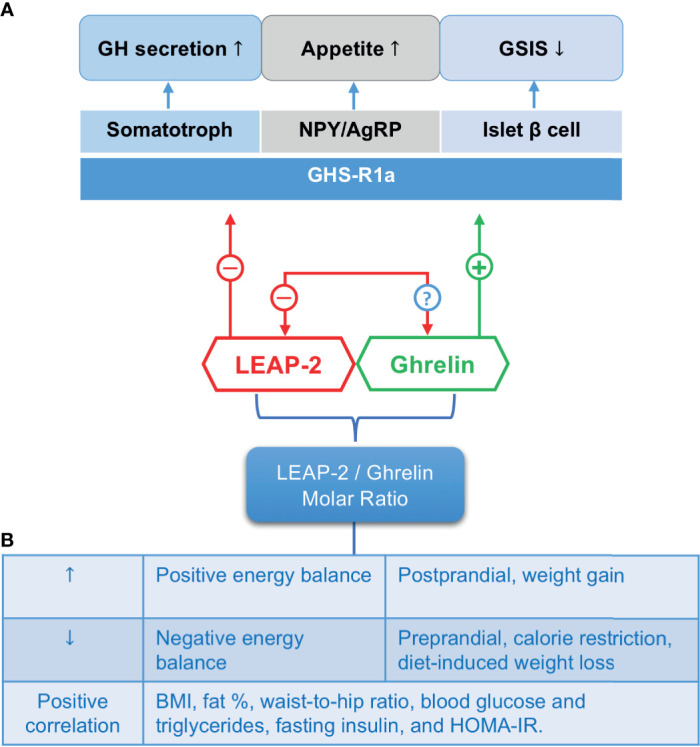
The counter-regulatory effects of LEAP-2 and ghrelin. (A) LEAP-2 blocks whereas ghrelin activates the GHS-R1a on target cells (e.g., somatotroph, NPY/AgRP neurons, and islet β cells) to exert biological functions on regulating GH secretion, appetite and GSIS, respectively. Ghrelin inhibits hepatic LEAP-2 mRNA expression, while LEAP-2’s effect on ghrelin expression is still unknown. (B) The LEAP-2/ghrelin molar ratio. This ratio changes accordingly to energy status and correlates positively with BMI and some metabolic parameters. ↑, increase; ↓, decrease; -, inhibit; +, activate; ?, unknown; GH, growth hormone; GSIS, glucose-stimulated insulin secretion; NPY/AgRP, neuropeptide Y/agouti-related protein; BMI, body mass index; HOMA-IR, homeostatic model assessment for insulin resistance.
