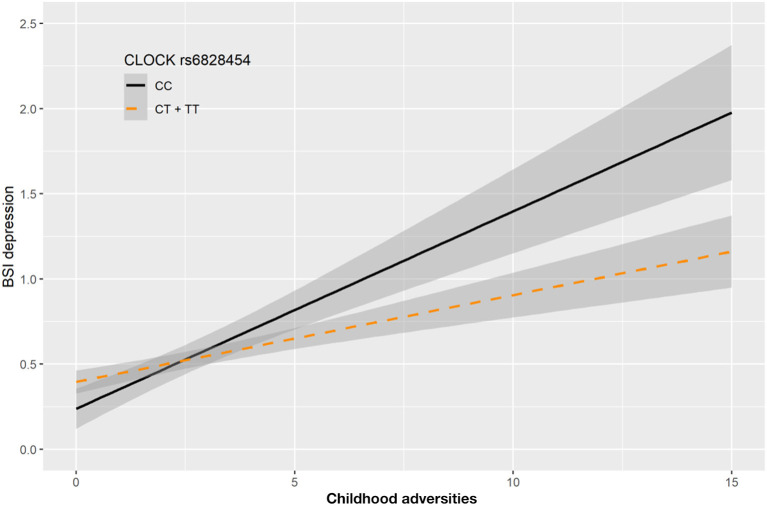
Figure 4.
Linear regression indicated a significant interaction between top SNP rs6828454 of a clump containing 9 SNPs in the CLOCK gene and exposure to childhood adversities on current depression symptoms (BSI-dep) in the recessive model, with the minor C allele being a risk allele. Linear regression indicated a significant interaction between CLOCK rs6828454 genotype and childhood adverse life events (CHA) on current depression scores according to the recessive model as top SNP (p = 0.0006, FDR Q = 0.0118). Homozygous presence of the minor C allele was associated with higher depression scores in subjects exposed to more severe childhood adverse events conveying a risk effect. On the vertical axis weighted depression (BSI-Dep) scores are shown. The horizontal axis shows childhood adverse life events (CHA) as measured by an instrument derived from the CTQ (30). BSI-Brief symptom inventory. Gray shading denotes 95%CI.