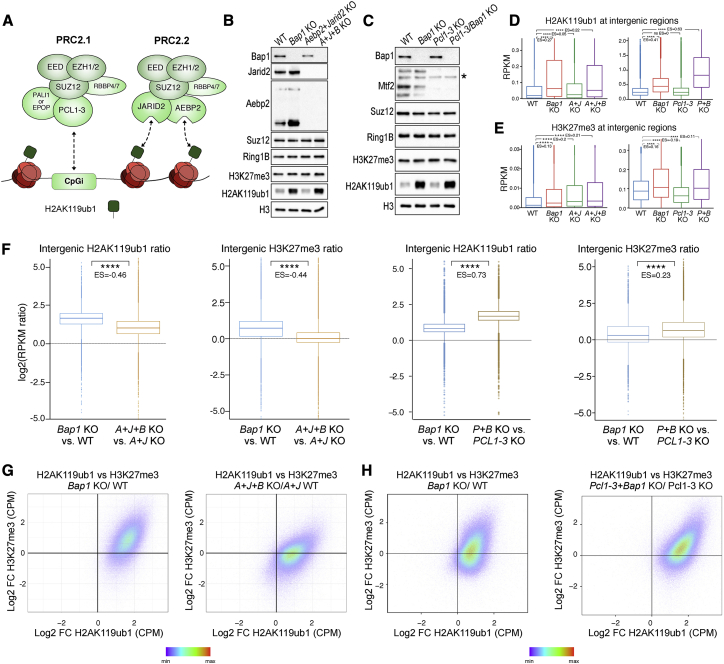
Figure 5.
PRC2 sub-complexes differentially contribute to the BAP1-dependent intergenic H3K27me3 deposition
(A) Cartoon showing divergent compositions of the PRC2.1 and PRC2.2 complexes and their differing affinities for chromatin features.
(B) Western blot analysis with the indicated antibodies on total protein extracts from the Bap1 KO, Aebp2+Jarid2 (A+J) KO, Aebp2+Jarid2+Bap1 (A+J+B) KO, and matching WT ESCs.
(C) Western blot analysis with the indicated antibodies on total protein extracts from the indicated ESC lines.
(D) Boxplots representing H2AK119ub1 ChIP-seq RPKM levels in the indicated cell lines at intergenic sites (n = 38,068).
(E) Boxplots representing H3K27me3 ChIP-seq RPKM levels in the indicated cell lines at intergenic sites (n = 38,068).
(F) Boxplots showing the log2 fold change RPKM ratio for H2AK119ub1 or H3K27me3 in the indicated cell lines (A = Aebp2, J = Jarid2, P = Pcl1-3) at intergenic regions (n = 38,068).
(G) Genome-wide comparison of ChIP-seq signal using 5 kb windows. Log2 fold change H2AK119ub1 ChIP-seq for the Aebp2/Jarid2/Bap1 KO versus Aebp2/Jarid2 KO and the matching Bap1 KO versus WT comparison (x axis) plotted against log2 fold change of H3K27me3 ChIP-seq (y axis). Each dot represents one 5 kb window.
(H) Genome-wide comparison of ChIP-seq signal using 5 kb windows. Log2 fold change H2AK119ub1 ChIP-seq for the Pcl1-3/Bap1 KO versus Pcl1-3 KO and the matching Bap1 KO versus WT comparison (x axis) plotted against log2 fold change of H3K27me3 ChIP-seq (y axis). Each dot represents one 5 kb window.
See also Figure S4.