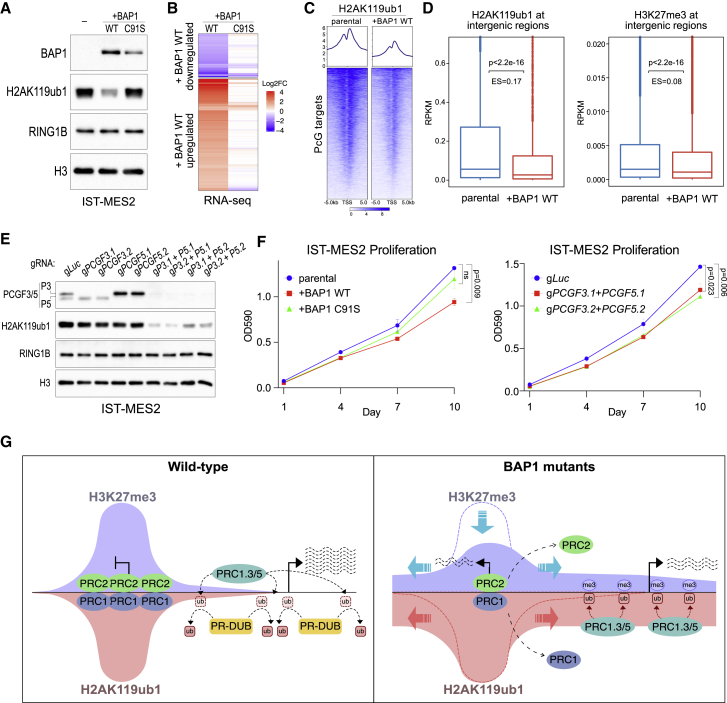
Figure 7.
Bap1 null mesothelioma growth requires PCGF3/5-dependent H2AK119ub1 accumulation
(A) Western blot using the indicated antibodies in whole-cell lysates of the BAP1 null IST-MES2 mesothelioma cell line with either parental or BAP1 WT/C91S overexpression.
(B) RNA-seq heatmap of those genes differentially expressed in +BAP1 WT IST-MES2 versus parental IST-MES2.
(C) Metaplots and heatmaps representing normalized ChIP-seq intensity for H2AK119ub1 in the indicated cell lines.
(D) Boxplots representing H2AK119ub1 (left) or H3K27me3 (right) ChIP-seq RPKM levels in the indicated cell lines at intergenic sites.
(E) Western blot using the indicated antibodies in IST-MES2 cell line whole-cell lysates following knockout of PCGF3 or PCGF5 in the indicated combinations.
(F) Growth curves measured using crystal violet staining (λ = 590 nm) of the indicated cell lines. Data are represented as mean ± SD.
(G) Model of the dual role of BAP1 mode of action on transcription. BAP1 is essential for the spatial maintenance of H2AK119ub1 and H3K27me3. Spurious redistribution of these in the absence of BAP1, directed by the PCGF3/5-PRC1 and PRC2.2 complexes, promotes chromatin compaction and a general repression of transcription (Trithorax phenotype) while simultaneously allowing derepression of selected Polycomb target genes (Polycomb phenotype).