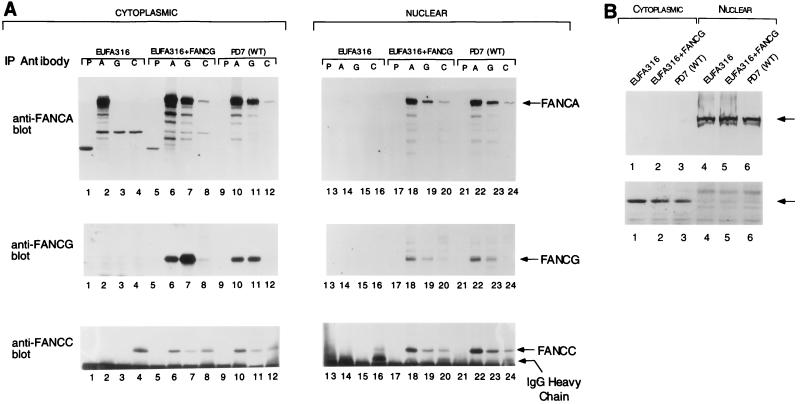
FIG. 3.
FANCG is a component of the cytoplasmic and nuclear FANCA/FANCC protein complex. (A) The indicated lymphoblast lines, including EUFA316 (FA-G cells), EUFA316 corrected with the FANCG cDNA (FA-G + FANCG), or PD7 (normal adult control) were lysed and fractionated into cytoplasmic and nuclear fractions. Proteins from each fraction were immunoprecipitated with control nonimmune (P), anti-FANCA (A), anti-FANCG (G), or anti-FANCC (C) serum. Proteins were resolved by sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis, transferred to nitrocellulose, and immunoblotted with anti-FANCA (upper panel), anti-FANCG (middle panel) or anti-FANCC (lower panel) serum. To demonstrate that the absence of the FANCA/FANCC interaction in FA-G cells is not simply due to the low expression level of FANCA and FANCC in these cells, three times more cytoplasmic extract (6 mg in 1 ml) was used for EUFA316 (lanes 1 to 4) than for the other two cell lines (lanes 5 to 12). (B) To ensure effective fractionation, samples from the indicated lymphoblast lines described in panel A were analyzed for topoisomerase levels (upper panel) and β-tubulin levels (lower panel). WT, wild type; IgG, immunoglobulin G; IP, immunoprecipitating.