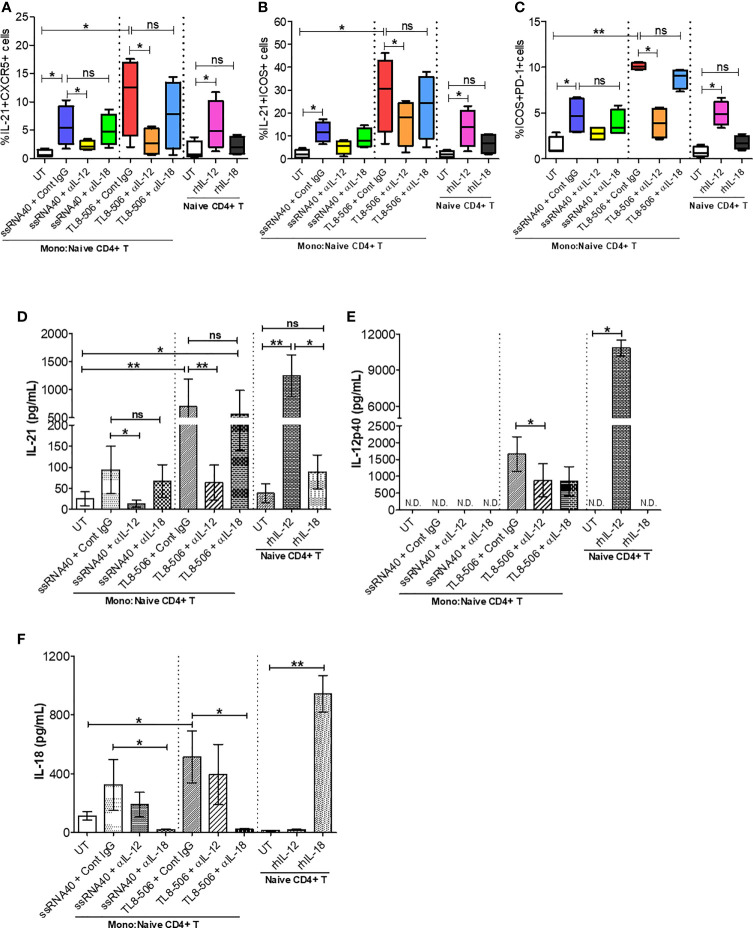
Figure 5.
TLR8 signaling promotes IL-12-dependent GC-like TFH cell differentiation and improved IL-21 production. Autologous naïve CD4+ T cells were isolated from PBMCs of HC (n=2) and CHB patients (n=2) and co-cultured with CD14+ enriched monocytes (as APCs, 2:1 ratio) previously stimulated with medium (UT, negative control), TLR8-specific ligands ssRNA40 or TL8-506 along with isotype control IgG, anti-IL-12 or anti-IL-18 neutralizing (blocking) Ab and cultured for 6 days in the presence of SEB followed by re-stimulation with PMA/Ion to activate TFH cells. Flow cytometry was carried out and the frequencies of cells co-expressing TFH markers are shown for (A) IL-21+CXCR5+, (B) IL-21+ICOS+ and (C) ICOS+PD-1+. Cytokine levels were quantified in the supernatants collected from monocyte-naïve CD4+ T co-cultures as well as naïve CD4+ T cell culture by Luminex multiplex immunoassay. Bar graph depicts the levels of (D) IL-21 (pg/mL), (E) IL-12p40 (pg/mL) and (F) IL-18 (pg/mL) secretion in response to TLR8-specific agonists and blocked by anti-IL-12, anti-IL-18 neutralizing Abs or upon incubation with human recombinant proteins IL-12 or IL-18. Statistical significance calculated by one-way ANOVA or Kruskal-Wallis test for comparison between stimulation conditions. P values ≤0.05*, 0.01** considered significant, ns, no significance; APCs, antigen-presenting cells; SEB, staphylococcal enterotoxin B; rhIL-12/IL-18, recombinant human protein IL-12/IL-18; Cont. IgG, isotype control IgG; N.D., not detected.