Fig. 1.
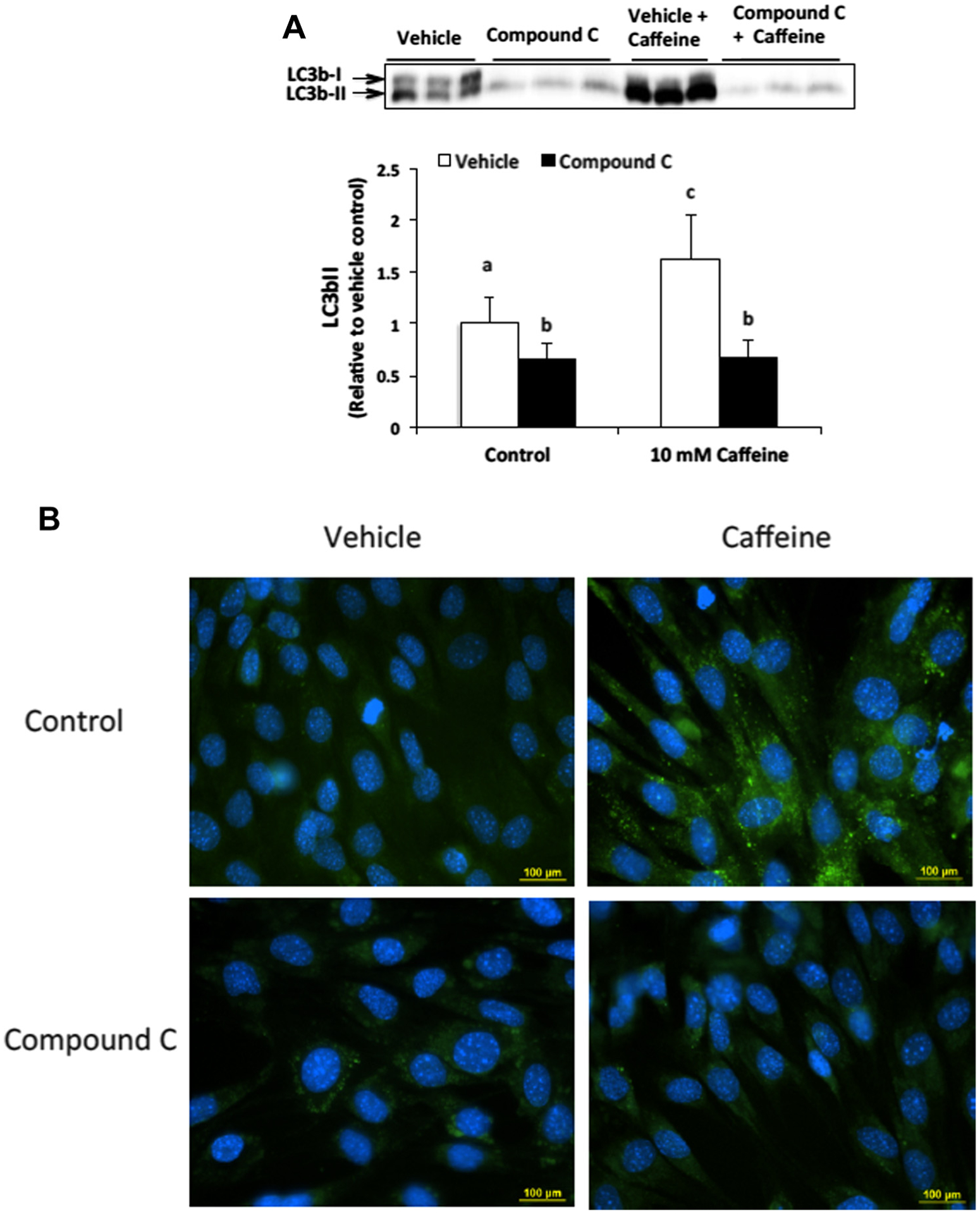
AMPK contributes to autophagy induction in caffeine treated skeletal muscle cells. (A) C2C12 myotubes were treated with either vehicle or Compound C (20 μM) alone or in combination with 10 mM caffeine for 6 h (n = 3). Western blot analysis revealed that caffeine significantly increased LC3b-II expression in an AMPK-dependent manner. Once a satisfactory image was obtained each membrane was stained with coomassie brilliant blue (R-250) and imaged for total protein assessment to allow each sample to be normalized to total protein content of each lane (data not shown). (B) Fluorescence microscopy analysis confirmed that Compound C inhibited autophagic vesicle formation in caffeine treated myotubes (n = 3). a–cIndicate significant difference between treatments without same letters (P < 0.05).
