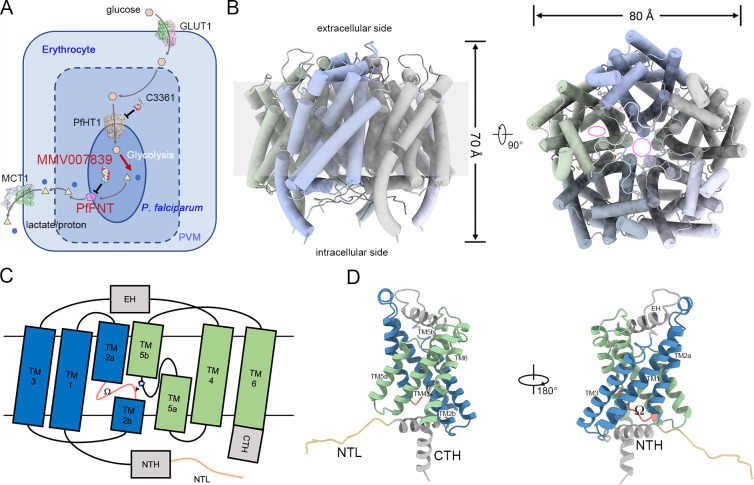
Fig 1. Overall structure of PfFNT.
(A) Hexose–monocarboxylate transport system of the P. falciparum–infected erythrocyte. Glucose and lactate are represented by orange hexagons and yellow triangles, respectively. Protons are presented by the blue circles. The magenta pentagon represents the PfFNT protein. Other reported structures, including human glucose transporter GLUT1 (PDB code: 4PYP), human monocarboxylate transporter MCT1 (PDB code: 6LZ0), and P. falciparum hexose transporter PfHT1 (PDB code: 6M2L), are presented as surface representations. Inhibitors of PfFNT (MMV007839) and PfHT1 (C3361) are displayed as sphere models. (B) Overall structure of pentameric PfFNT. The central tunnel of the pentamer and substrate translocation path in the protomer are indicated by pink circle and ellipse in the top view, respectively. (C) Topology diagram of a PfFNT protomer. The N-terminal and carboxyl-terminal TM segments are colored blue and green, respectively. Soluble helices, including the EH, NTH, and CTH, are colored gray. The NTL and Ω loops are colored sandy brown and salmon, respectively. Thr106 and His230 are presented as side chain models. (D) Cartoon representation of a PfFNT protomer. Components of the protomer are labeled in C. CTH, carboxyl-terminal helix; EH, extracellular helix; GLUT1, glucose transporter 1; MCT1, monocarboxylate transporter 1; NTH, N-terminal helix; NTL, N-terminal loop; PDB, Protein Data Bank; PfFNT, P. falciparum formate–nitrite transporter; PfHT1, P. falciparum hexose transporter 1; PVM, parasitophorous vacuole membrane; TM, transmembrane.