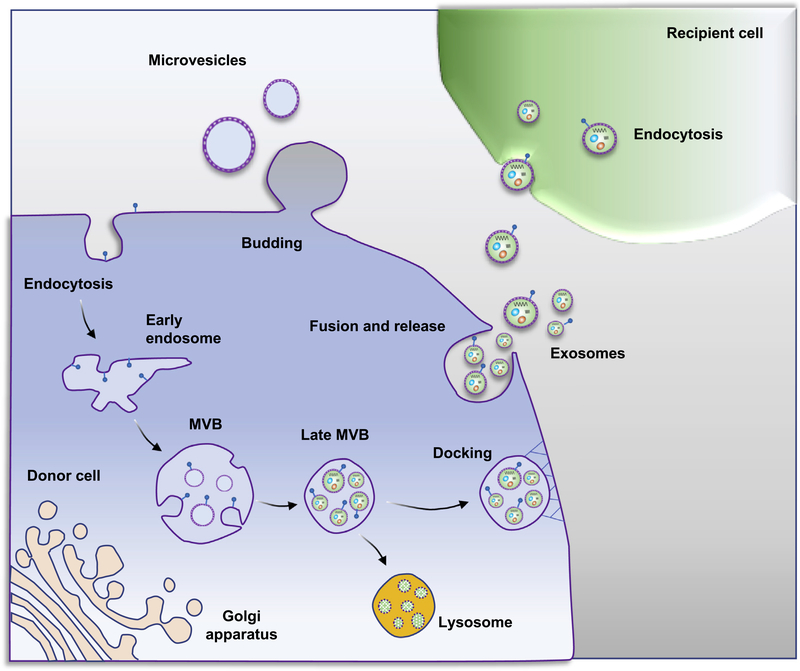
Figure 1. Exosome and microvesicle biogenesis pathways.
Microvesicles bud directly from the plasma membrane, and exosomes are generated by inward budding of the multivesicular body (MVB) lipid bilayer membrane. MVB fusion with the plasma membrane is a tightly regulated multistep process that includes MVB trafficking along microtubules and docking at the plasma membrane for further exosome release. Alternatively, MVBs can fuse with lysosomes as part of the degradative process. Initially, exosomes bind to the cell surface of recipient cells through protein-protein or receptor-ligand interactions, which can initiate signaling cascades that activate endocytotic pathways. The exosome cargo confers the biologic effects of exosomes on recipient cells.