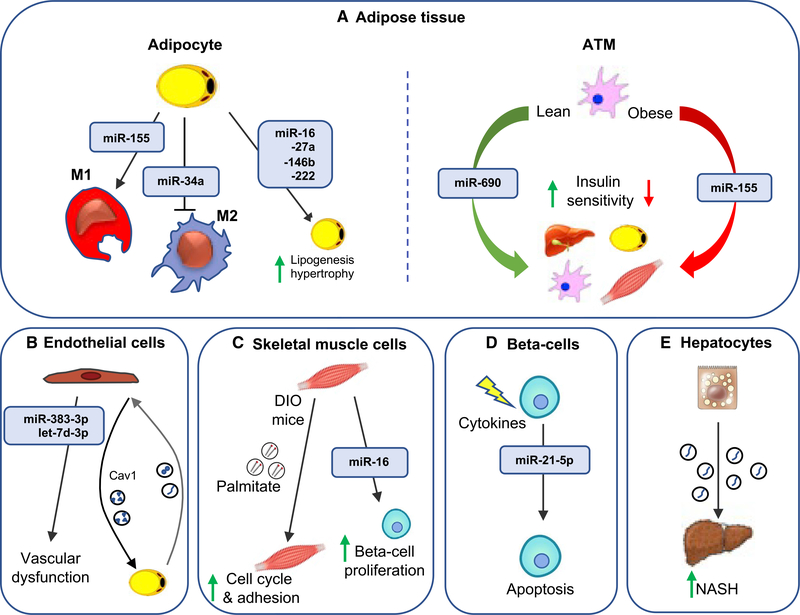
Figure 4. Exosomal miRNA effects on recipient cells.
Exosomal miRNAs mediate communication between donor cells and recipient cells, playing an important role in metabolic signaling.
(A) Adipocyte exosomal miRNAs can modulate macrophage polarization and lipogenesis and hypertrophy in adipocytes. Additionally, adipose tissue macrophage (ATM) exosomes can regulate insulin sensitivity through the delivery of miR-690 to the liver, adipocytes, ATMs, and skeletal muscle.
(B) Inflammatory factors induce the release of endothelial cell (EC) exosomes that contain miR-383–3p and let-7d-3p. ECs transfer cav1-containing exosomes to adipocytes, which reciprocate by releasing exosomes taken up by ECs.
(C) Skeletal muscle-derived exosomes induce cell cycle and adhesion in skeletal muscle as well as proliferation of isolated mouse beta cells.
(D) Cytokine-treated beta cell lines and human islets lead to enhanced secretion of exosomal miR-21–5p. Exosomes from cytokine-treated beta cells induce apoptosis in the recipient cells.
(E) Lipotoxic hepatocytes secrete exosomes that activate hepatic stellate cells, promoting the fibrotic NASH phenotype.