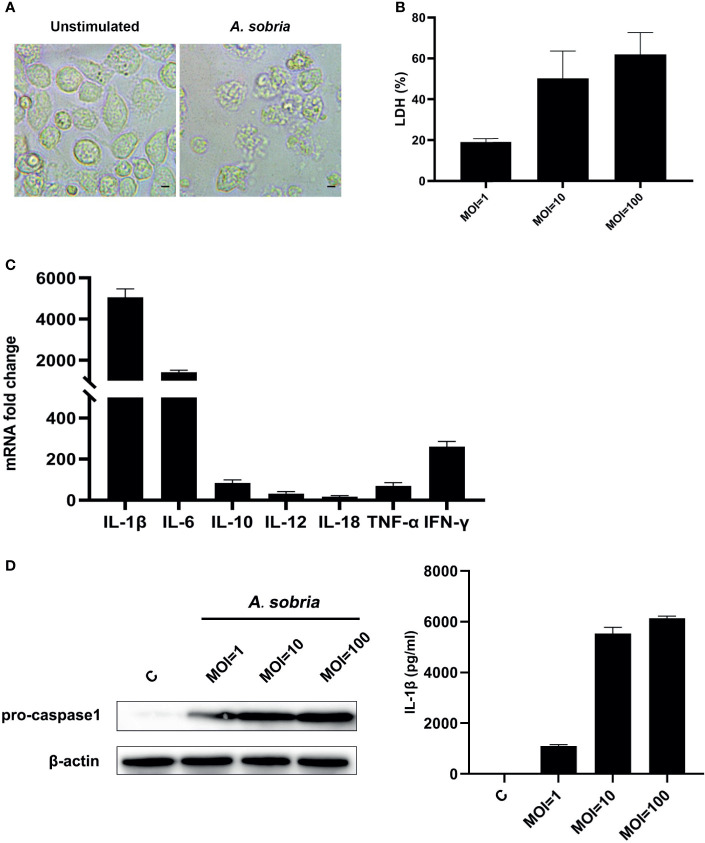
Figure 1.
A sobria triggered PMφs death and inflammatory response. PMφs were infected with A sobria (MOI = 1, 10, 100) for 90 min, and then A sobria was discarded. After washing three times with sterile PBS, PMφs were treated with gentamicin sulfate (100 μg/ml) containing RPMI 1640 maintenance medium for 2 h to kill residual A sobria and then replaced with gentamicin sulfate (20 μg/ml) containing RPMI 1640 maintenance medium for 12 h (A) Phase contrast images of unstimulated or A sobria–stimulated (MOI = 10) PMφs. Bar = 10 μm. (B) The cytotoxicity was evaluated by measuring the LDH release from A sobria–infected supernatants (MOI = 1, 10, 100). (C) RNA was extracted from infected cells (MOI = 10), and cDNA was synthesized for pro-inflammatory gene transcription levels analysis using qPCR. (D) Cells were lysed from infected cells (MOI = 0, 1, 10, 100), and protein was extracted for pro-IL-1β expression analysis using western blotting. Meanwhile, supernatants were harvested, and IL-1β protein levels were measured using ELISA. Data were presented as mean ± Standard Deviation from three independent assays.