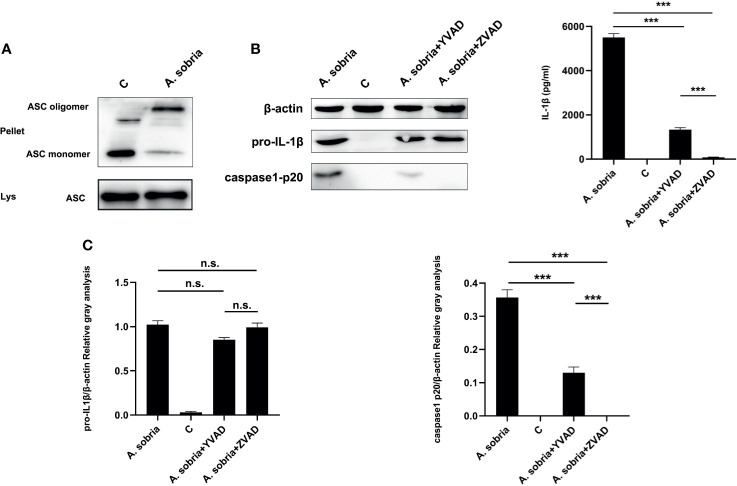
Figure 2.
A sobria–induced IL-1β secretion was regulated by ASC-dependent inflammasome activation. PMφs (4.5 × 106 cells/well in six-well plate) were pretreated with either Ac-YVAD-CHO (100 μM) or zVAD-fmk (10 μM) for 1 h, infected with A sobria (MOI= 10) for 90 min, and then A sobria was discarded. After washing three times with sterile PBS, PMφs were treated with gentamicin sulfate (100 μg/ml) containing RPMI 1640 maintenance medium for 2 h to kill residual A sobria and then replaced with gentamicin sulfate (20 μg/ml) containing RPMI 1640 maintenance medium for 12 h The activated caspase-1 p20 was detected in the supernatants using western blotting, and mature IL-1β p17 was detected in the supernatants using ELISA. No inhibitor treatment group was used as positive control group, and no A sobria inoculation group was used as negative control (C) group. (A) The ASC oligomerization levels were evaluated in the A sobria inoculation group and C group. Pellet represented cross-linked cell pellet, and Lys represented lysed cells. (B) The protein expression of caspase-1 p20, pro-IL-1β, and mature IL-1β was detected in the inhibitor pretreatment groups, A sobria inoculation group, and C group. (C) The relative gray values of caspase-1 p20 and pro-IL-1β were normalized to β-actin through Image. Data were presented as mean ± Standard Deviation from three independent assays with three technical repeats. Significant difference was analyzed using SPSS software, and graph was generated using GraphPad Prism 8 software. *** represents p < 0.001, and n.s. represents p > 0.05.