Figure 6.
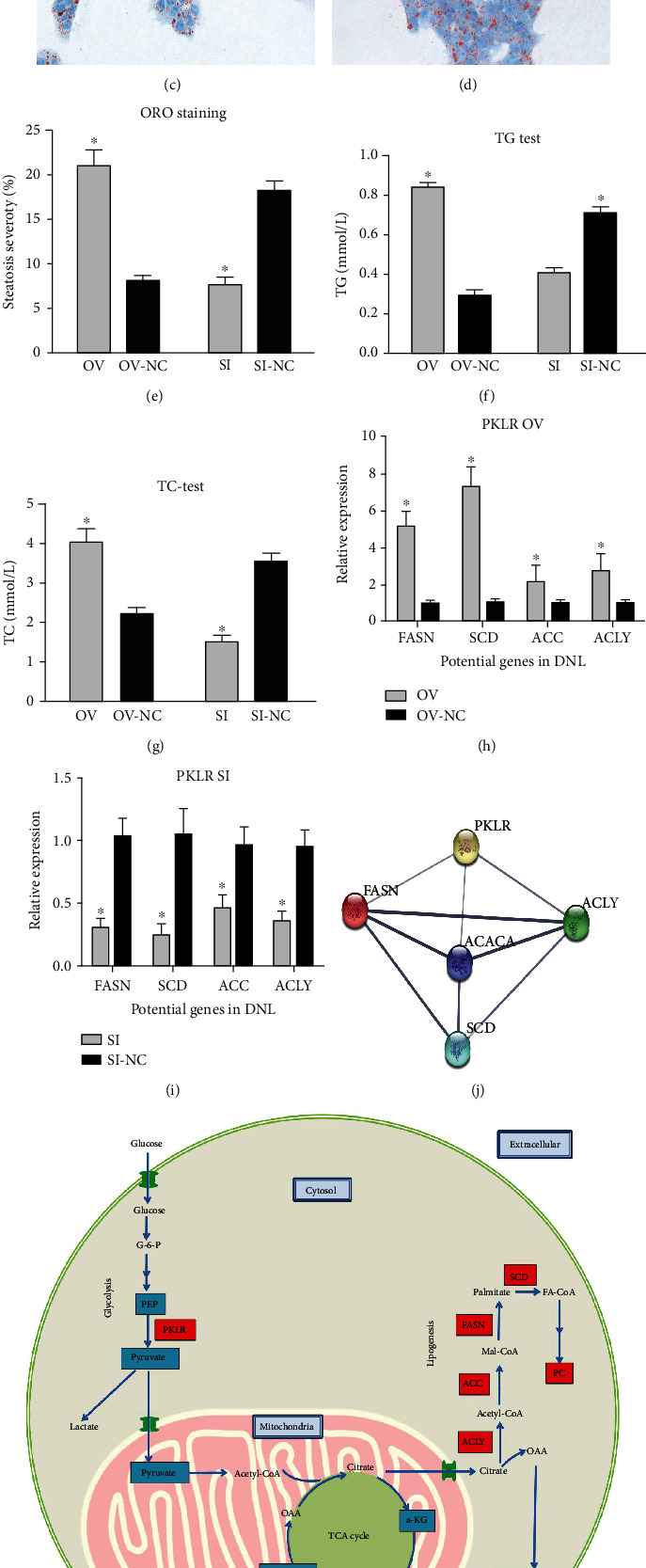
Genetic impact of pyruvate kinase L/R on the process of de novo lipogenesis. HepG2 cells with PKLR alteration were treated by high-glucose medium (50 mmol/L), respectively, for 48 hours. And lipogenic severity was evaluated by ORO staining. (a) ORO staining for cells with overexpressed PKLR. (b) ORO staining for NC cells with overexpressed PKLR. (c) ORO staining for cells with suppressed PKLR. (d) ORO staining for NC cells with suppressed PKLR. (e) Comparison of lipogenic severity between cells with overexpressed/suppressed PKLR and their corresponded NC. (f) Comparison of hepatic TG between cells with overexpressed/suppressed PKLR and their corresponded NC. (g) Comparison of hepatic TC between cells with overexpressed/suppressed PKLR and their corresponded NC. (h) Comparison of key genes that located on DNL process between cells with overexpressed PKLR and their corresponded NC. (i) Comparison of key genes that located on DNL process between cells with suppressed PKLR and their corresponded NC. (j) PPI network between PKLR and selected genes that located on DNL process. (k) Speculated mechanism for the impact of PKLR on DNL process. Stained cells were observed and scanned under a microscope (magnification: 400x); ∗ represented statistical significance for comparisons between targeted cells and corresponded NC (P < 0.05); TG and TC were both evaluated in systems with 100 000 cells in 100 μL of solution buffer. Frames in red represented the molecules with upregulations; frames in blue represented the molecules with downregulations. Abbreviations: a-KG: alpha-ketoglutarate; DNL: de novo lipogenesis; G-6-P: glucose-6-phosphate; ORO: oil red O; NC: negative control; OAA: oxaloacetate; PEP: phosphoenolpyruvate; PC: phosphatidylinositol; PKLR: pyruvate kinase L/R; PPI: protein-protein interaction; TCA: tricarboxylic acid cycle; TC: total cholesterol; TG: triglyceride.
