Figure 3.
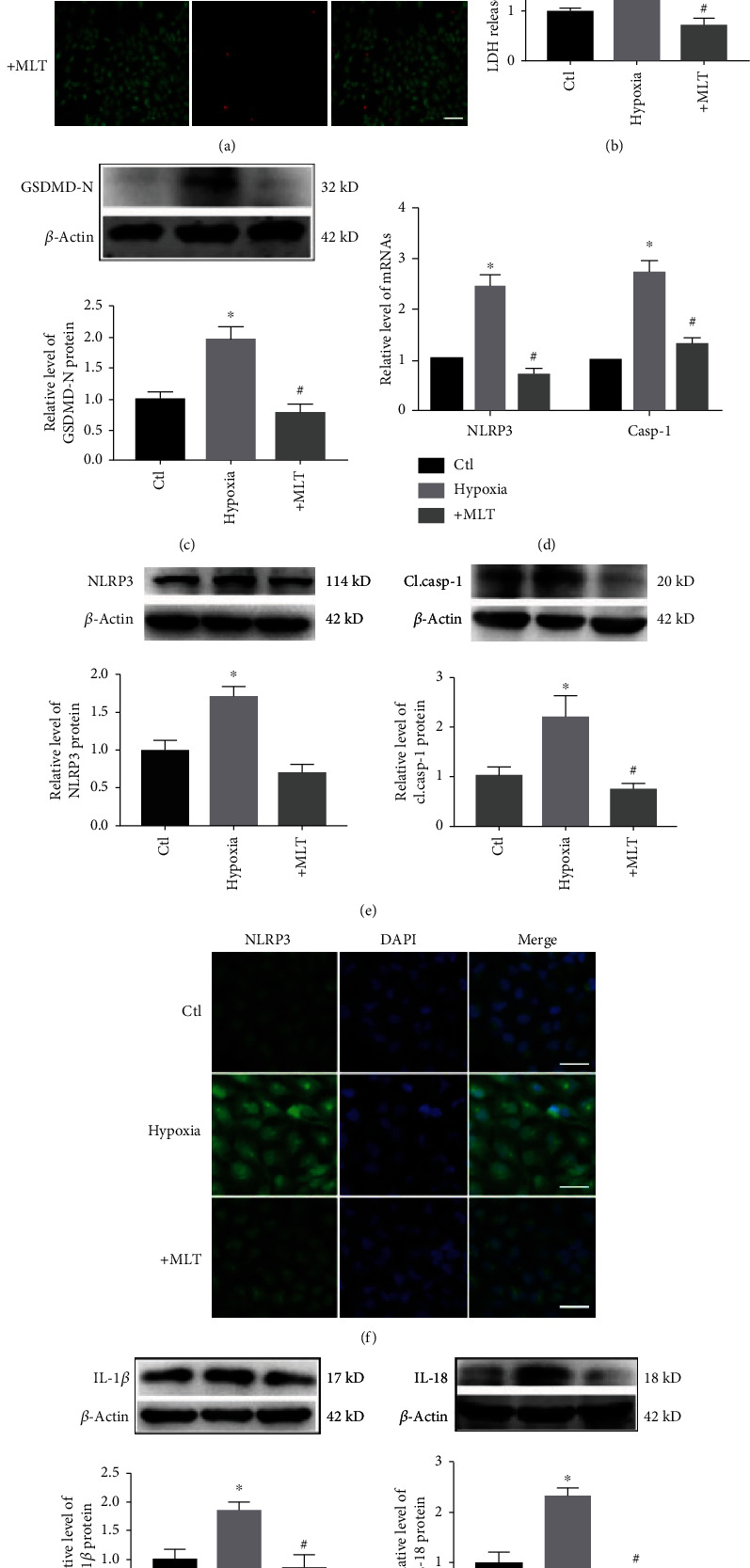
Effect of melatonin on NLRP3 inflammasome-mediated cardiac pyroptosis in H9C2 cells exposed to hypoxia. (a) Melatonin reduced hypoxia-induced cardiomyocyte loss. Live cells were stained with calcein-AM (green), and dead cells were stained with EthD-III (red). Scale bar, 40 μm. (b) Melatonin treatment decreased the release of LDH in H9C2 cells. ∗P < 0.05 vs. ctl, #P < 0.05 vs. hypoxia. Number of trials = 3. (c) GSDMD-N levels were decreased by melatonin treatment. ∗P < 0.05 vs. ctl, #P < 0.05. Number of trials = 3. (d) The mRNA levels of NLRP3 and caspase-1 in the different groups were detected by real-time PCR. ∗P < 0.05 vs. ctl, #P < 0.05. Number of trials = 3. (e) Melatonin treatment reduced the levels of NLRP3 and cl.casp-1 in hypoxia-treated H9C2 cells. ∗P < 0.05 vs. ctl, #P < 0.05 vs. hypoxia. Number of trials = 3. (f) NLRP3 levels were detected by immunofluorescence. Scale bar, 50 μm. (g) The levels of IL-1β and IL-18 were decreased by melatonin in H9C2 cells. ∗P < 0.05 vs. ctl, #P < 0.05 vs. hypoxia. Number of trials = 3. cl.casp-1: cleaved caspase-1; MLT: melatonin.
