Figure 5: AHR agonism promotes an ILC1 phenotype in vivo.
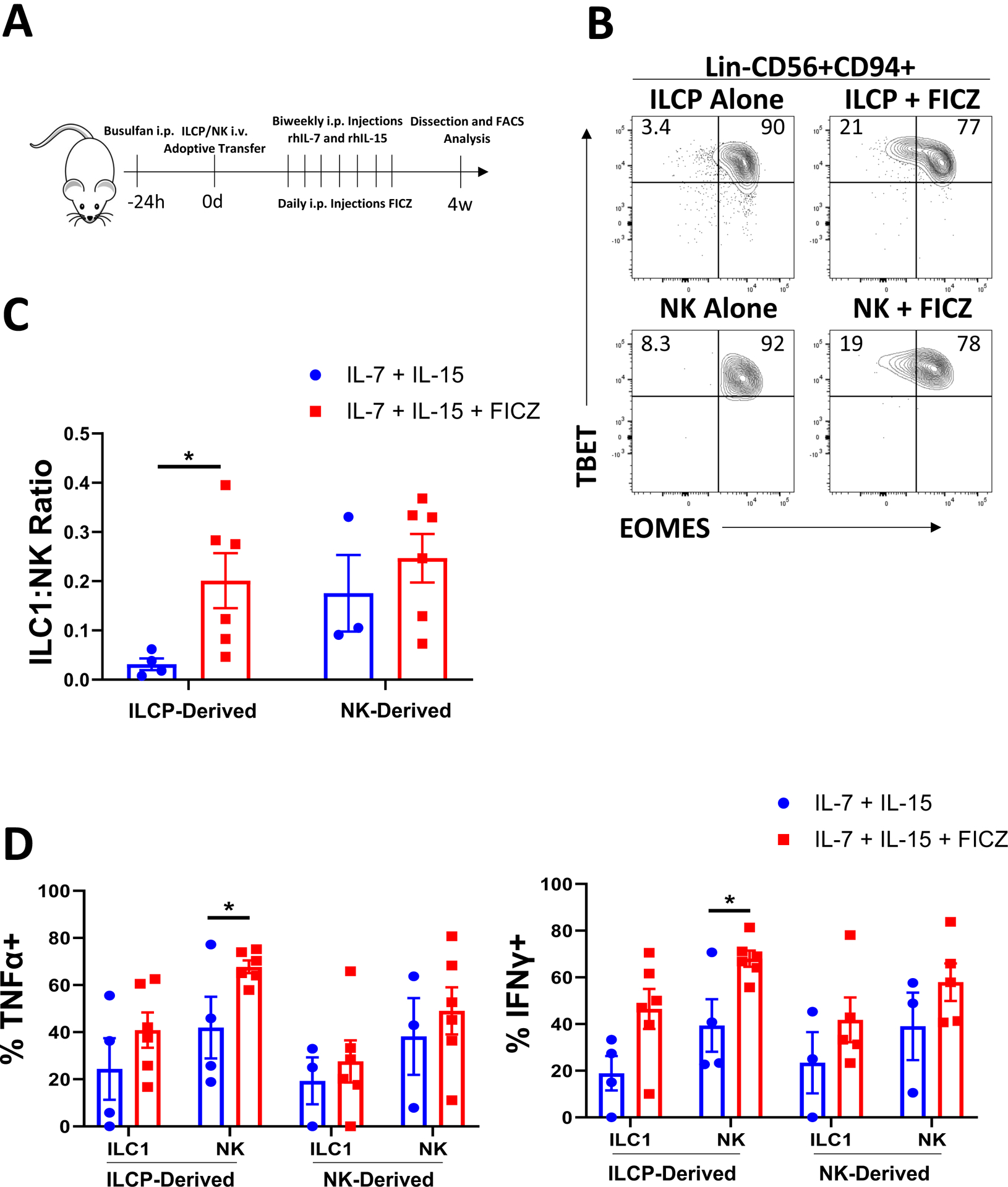
A) Schematic of in vivo studies. ILCPs (Lin-NKp80-CD294-KLRG1-NKp44-CD94−CD16−CD117+) and CD56bright NK cells (Lin-CD56+CD94+CD16−) were isolated from normal peripheral blood of 5 independent donors and adoptively transferred into NSG mice ± daily I.P. injections of FICZ (3 μg/mouse) or vehicle with biweekly injections of IL-7 and IL-15 for 4 weeks. At harvest, bone marrow was harvested and analyzed via flow cytometry for Group 1 human ILCs.
B) Representative flow plots of TBET and EOMES expression for human Lin-CD56+CD94+ cells derived from ILCPs or CD56bright NK cells ±FICZ.
C) Summary of ILC1:NK ratios comparing control conditions to FICZ-treated mice.
D) Summary data of TNFα and IFNγ expression determined by flow cytometry from ILCP- or CD56bright-derived NK cells and ILC1s from control or AML conditions.
n=3–5 (some mice excluded due to poor engraftment), *p<0.05. Error bars represent ±SEM.
