Figure 3. Focal expression of Bet1L at NMJs in the skeletal muscle of ALS model rats.
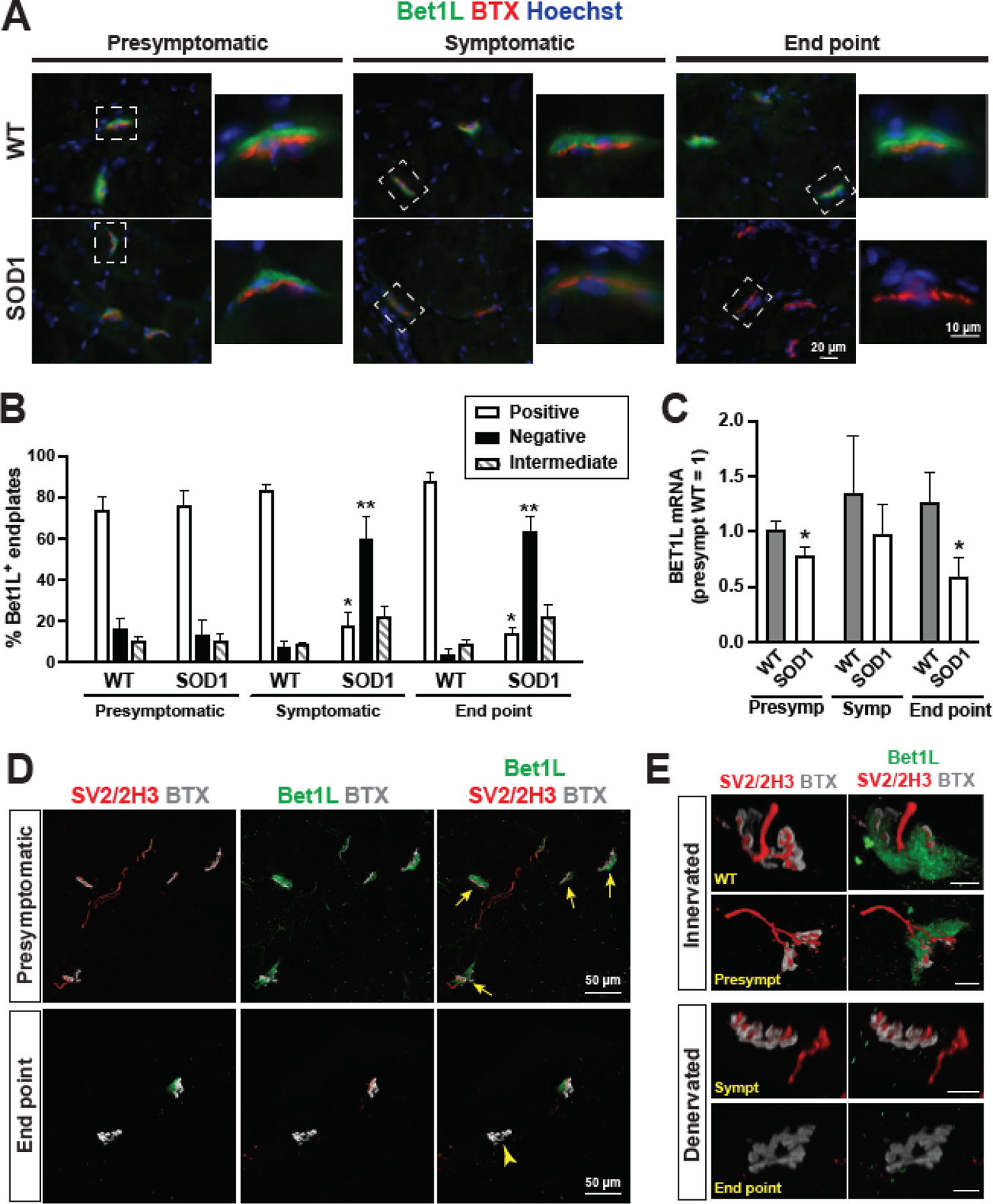
(A) Immunohistochemistry in cross-sections of SOD1G93A tibialis anterior muscles showed that Bet1L (green) was localized to the NMJ, as indicated by BTX (red). Expression of Bet1L was decreased in symptomatic and end point SOD1G93A rats compared to presymptomatic and WT controls. (B) Immunostained muscle sections were counted for Bet1L-positive, intermediate, or negative NMJs at each time point according to representative images in (A). By the symptomatic time point, the amount of Bet1L-positive NMJs was significantly reduced. Muscle sections from 8 WT and 8 SOD1G93A rats were counted at each time point, with an average of 81 NMJs counted per animal. *P<0.05 vs. other positive groups. **P<0.05 vs. other negative groups. (C) Tibialis anterior muscles were harvested at presymptomatic, symptomatic, and end point disease stages and homogenized to collect RNA for RT-qPCR to detect Bet1L gene expression. Results were normalized to the mean value of the WT presymptomatic rats. N = 8 rats per time point (4 male and 4 female). *P<0.05 vs. counterpart WT, according to unpaired Student’s t test. (D) Immunohistochemistry for Bet1L co-localization with axonal markers SV2 and 2H3 for comparison of Bet1L expression at innervated NMJs (yellow arrows) in presymptomatic rats and denervated NMJs (a yellow arrow head) in end stage SOD1G93A rats. (E) Representative images of Bet1L staining at innervated and denervated NMJs along disease progression compared to a WT control NMJ. Scale bars = 10 μm.
