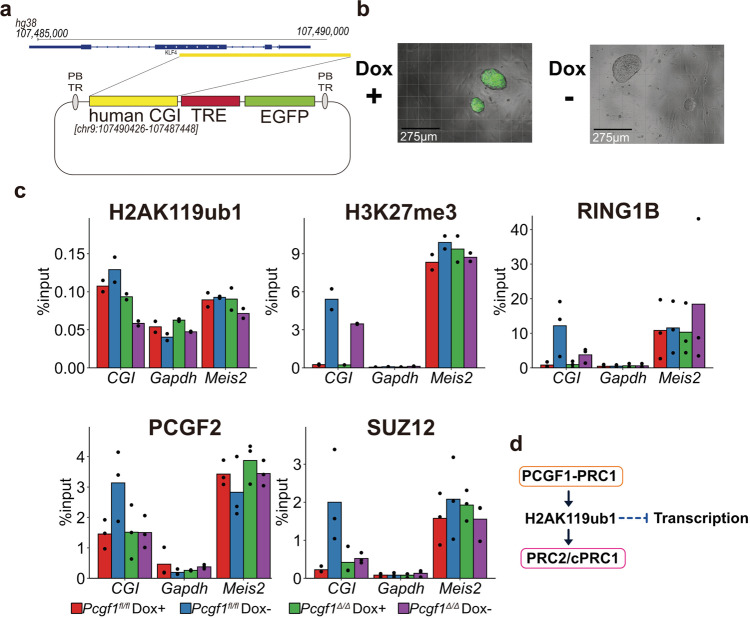
Fig. 5. Transcriptional downregulation at cis-regulatory elements facilitates PRC2 recruitment to a CGI in a PCGF1-dependent manner.
a Schematic representation of the drug-inducible reporter construct. The vector contains a human KLF4 CpG island (human CGI), a Dox-inducible promoter (TRE), and an EGFP gene. This reporter vector was stably integrated into Pcgf1-KO ESCs by piggyBAC transposase. b Dox-dependent expression of EGFP from the reporter construct in ESCs. Representative micrographs were shown. Experiments were repeated independently at least 2 times with the same results. c Dox- and PCGF1-dependent regulation of the accumulation of H2AK119ub1, H3K27me3, RING1B, SUZ12, and PCGF2 at the CGI of the reporter gene in ESCs. Bar graphs for ChIP-qPCR results for H2AK119ub1, H3K27me3, RING1B, SUZ12, and PCGF2 at the human CGI of the reporter, Gapdh and Meis2 in WT (Pcgf1fl/fl) or Pcgf1-KO (Pcgf1∆/∆) ESCs in the absence or presence of Dox (-Dox and +Dox, respectively) are shown. Data are represented as mean ± SEM (n = 3). d Schematic summary for the role of PCGF1-PRC1 to link H2AK119ub1 with PRC2 revealed in this study. PCGF1-PRC1 mediates H2AK119ub1 deposition and contributes to the consolidation of gene silencing via undefined mechanisms (indicated by dotted line) and in turn recruitment of PRC2 and cPRC1 (indicated by an arrow). H2AK119ub1-dependent recruitment of PRC2 and canonical PRC1 is inhibited by transcriptional activity (indicated by a solid line).