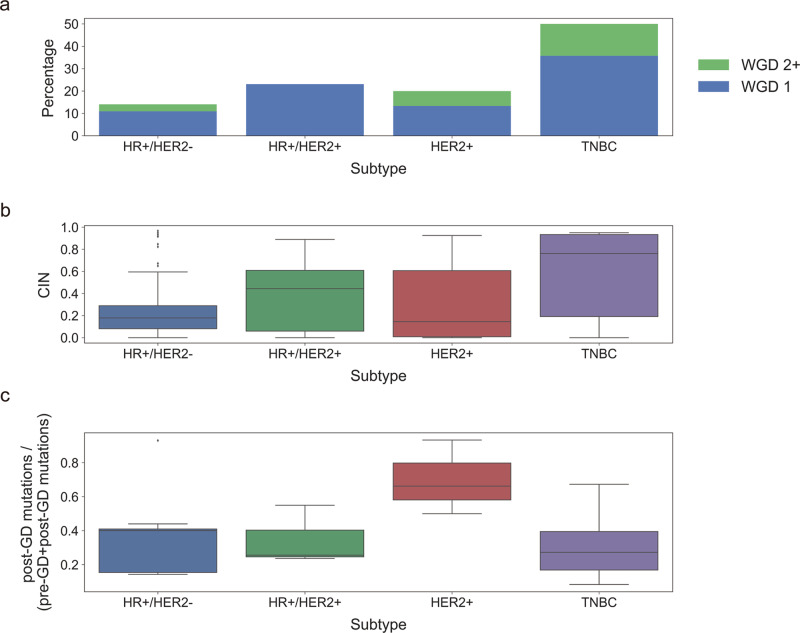
Fig. 2. Prevalence of whole-genome doubling (WGD), level of chromosomal instability (CIN), and timing of WGD across breast cancer subtypes.
a Stacked bar plots show the fraction (y-axis) of samples harboring WGD across subtypes (x-axis). WGD 1 (blue) indicates 50% or more of the autosomal tumor genome with a major copy number of two, while WGD 2 + (green) indicates severe doubling with major copy number >2. b Box plots indicate the level of CIN (range, 0–1; y-axis) across subtypes (x-axis). c Box plots indicate the timing of WGD in each subtype. Timing was estimated based on the fraction of mutations occurring post-WGD compared to pre- and post-WGD combined. Overall, 64 HR + /HER2- (hormone receptor-positive/human epidermal growth factor receptor-negative), 13 HR + /HER2 + , 15 HER2 + , and 14 TNBC (triple-negative breast cancer) samples were used to perform analyses in a–c.