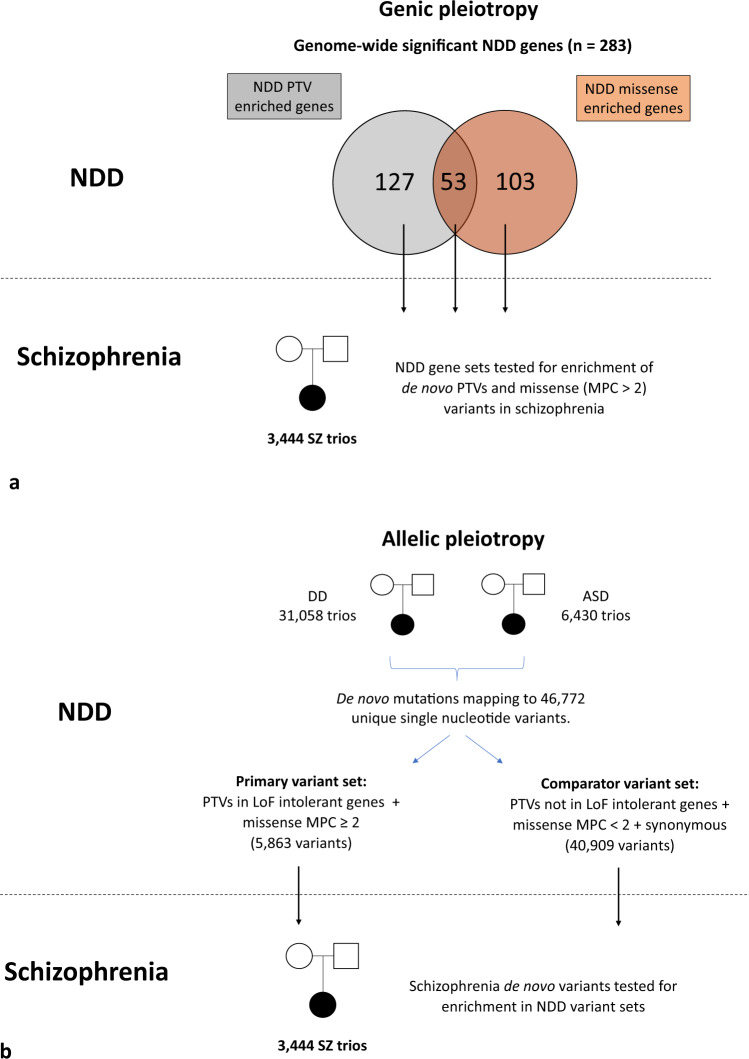
Fig. 1. Study design for analysis of genic and allelic pleiotropy.
a Study design for analysis of genic pleiotropy. Genes enriched for protein-truncating variants or missense variants in neurodevelopmental disorders with a P value <2.5 × 10−6 were identified from the Deciphering Developmental Disorders study14. For each NDD gene set, the observed and expected number of de novo variants in 3444 schizophrenia trios was compared using a two-sided two-sample Poisson rate ratio test. See Methods for further details. b Study design for analysis of allelic pleiotropy. Neurodevelopmental disorder variants were defined as de novo mutations reported in the largest sequencing studies of developmental disorders14 and autism spectrum disorders32. Neurodevelopmental disorder variants were stratified into a NDD primary variant set, defined as those alleles annotated as protein-truncating variants affecting loss-of-function intolerant genes or missense variants with an MPC score ≥2. The remaining neurodevelopmental disorder variants (protein-truncating variants not affecting loss-of-function intolerant genes, missense variants with an MPC score ≤2 and synonymous variants) were grouped into a NDD comparator variant set. The observed and expected number of schizophrenia de novo variants overlapping alleles within each NDD variant set was compared using a two-tailed Poisson exact test. See Methods for further details. NDD, neurodevelopmental disorder; SZ, schizophrenia; DD, developmental disorder; ASD, autism spectrum disorder; PTV, protein-truncating variant; MPC, “Missense badness, Polyphen-2, Constraint” pathogenicity score29.