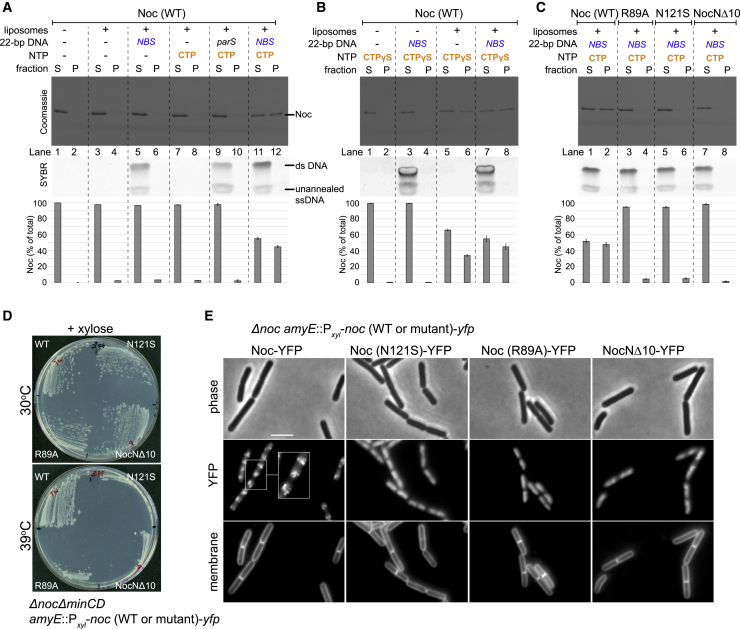
Figure 3.
Noc binds liposomes in the presence of CTP and NBS DNA, and the phenotypic effects of the Noc variants
(A) Analysis of B. subtilis Noc binding to membranes by a liposome co-sedimentation assay. A premix of 0.75 μM B. subtilis Noc protein ± 1.0 μM 22 bp linear parS/NBS DNA ± 1.0 mM CTP ± 1.0 mg/mL liposomes was incubated at 22°C for 5 min before ultracentrifugation. The resulting supernatant (S) and pellet (P) fractions were analyzed using SDS-PAGE. Samples were also loaded onto a 20% TBE PAGE, and the gel was subsequently stained with Sybr Green for DNA. Quantification of Noc in each fraction is shown below each representative image. Error bars represent SEM from three replicates.
(B) Same as (A), but 1.0 mM CTPɣS was used instead.
(C) Other Noc variants, Noc (R89A), Noc (N121S), and NocNΔ10, were also analyzed in a liposome co-sedimentation assay.
(D) Complementation of noc in a ΔnocΔminCD background. Strains ΔnocΔminCD amyE::Pxyl-noc (WT or mutant)-yfp were streaked on nutrient agar plates supplemented with 0.5% xylose and incubated at 30°C or 39°C.
(E) Cellular localization of YFP-labeled Noc (WT or mutants). Representative images of Δnoc amyE::Pxyl-noc (WT or mutant)-yfp cells grown in the presence of 0.5% xylose. Cell membranes were stained with FM5-95. Scale bar, 3 μm. Inset shows a magnification of a section of cells.