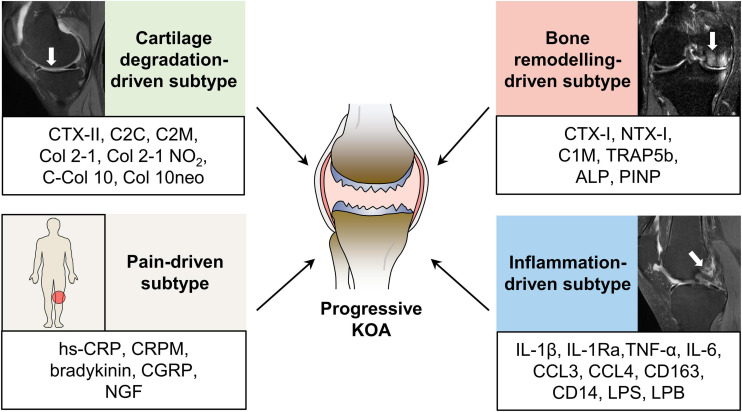
FIGURE 2.
Molecular subtypes of progressive KOA. Increasing evidence suggests that progressive KOA patients fall into several subtypes based on the identified molecular profiles, including cartilage degradation-driven subtype, bone remodeling-driven subtype, inflammation-driven subtype, and pain-driven subtype. Representative molecules are listed in the box bellow the MRI manifestation of each subtype. ALP, alkaline phosphatase; CCL3, CC-chemokine ligand 3; CCL4, CC-chemokine ligand 4; Col 2-1 NO2, the nitrated form of Col 2-1; C-Col 10, C-terminus of collagen X; Col 10neo, a neoepitope of collagen 10; CGRP, calcitonin gene-related peptide; CRPM, the fragment of C-reactive protein; CTX-I, C-telopeptide of Col-I; CTX-II, C-telopeptide fragments of Col-II; C2C, the cleavage neoepitope of collagen II; C1M, the product of collagen I degraded by matrix metalloproteinases; C2M, the fragments of collagen II degraded by matrix metalloproteinases; hs-CRP, high sensitive C-reactive protein; IL-1β, interleukin 1β; IL-1Ra, IL-1 receptor antagonist; IL-6, interleukin 6; KOA, knee osteoarthritis; LPS, lipopolysaccharide; LPB, LPS binding protein; MRI, magnetic resonance imaging; NGF, nerve growth factor; NTX-I, N-telopeptide of Collagen I; PINP, N-terminal collagen type I extension propeptide; TNFα, tumor necrosis factor α; TRAP5b, tartrate resistant acid phosphatase 5b.