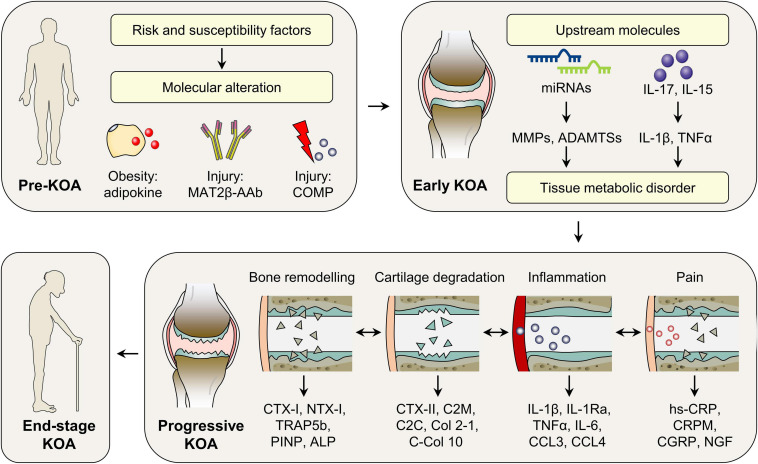
FIGURE 3.
Molecular classification of KOA. According to the temporal alteration of representative molecules during disease initiation and progression, KOA could be classified into pre-KOA, early KOA, progressive KOA, and end-stage KOA. In pre-KOA, risk factors-related molecules, such as adipokines, COMP, and MAT2β-AAb, can be detected in body fluids, which may provide evidence for KOA prediction. In early KOA, molecules can reflect the ongoing pathogenesis, when symptoms and imaging information are ambiguous. Based on the major pathophysiology in patient clusters, progressive KOA is further classified into four subtypes, i.e., cartilage degradation-driven subtype, bone remodeling driven subtype, inflammation-driven subtype, and pain-driven subtype, suggesting different treatment options in future clinical setting. ADAMTSs, a disintegrin and metalloproteinase with thrombospondin motifs; ALP, alkaline phosphatase; CCL3, CC-chemokine ligand 3; CCL4, CC-chemokine ligand 4; C-Col 10, C-terminus of collagen X; CGRP, calcitonin gene-related peptide; COMP, cartilage oligomeric matrix protein; CRPM, the fragment of CRP; CTX-I, C-telopeptide of Col-I; CTX-II, C-telopeptide fragments of Col-II; C2C, the cleavage neoepitope of collagen II; C2M, the fragments of collagen II degraded by matrix metalloproteinases; hs-CRP, high sensitive CRP; IL-1β, interleukin 1β; IL-1Ra, IL-1 receptor antagonist; IL-6, interleukin 6; IL-15, interleukin 15; IL-17, interleukin 17; KOA, knee osteoarthritis; MAT2β-AAb, methionine adenosyltransferase two beta autoantibody; miRNAs, microRNAs; MMPs, matrix metalloproteinases; NGF, nerve growth factor; NTX-I, N-telopeptide of Collagen I; PINP, N-terminal collagen type I extension propeptide; TNFα, tumor necrosis factor α; TRAP5b, tartrate resistant acid phosphatase 5b.