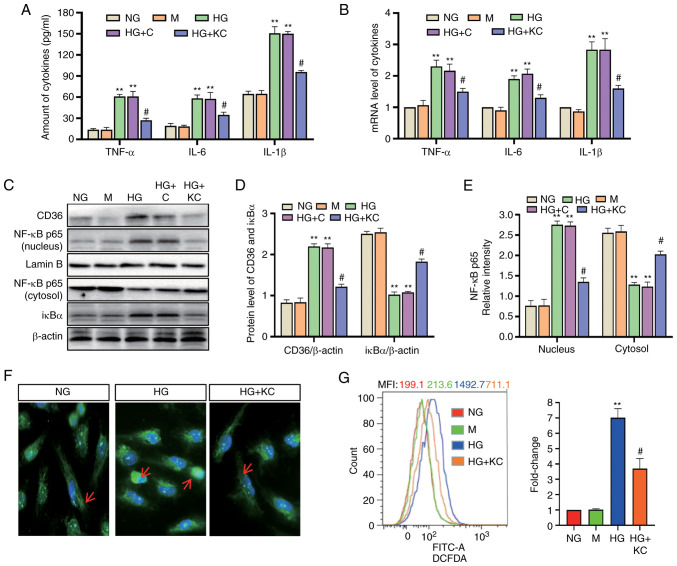
Figure 2.
Knockout of CD36 prevents NF-κB-mediated inflammatory responses and ROS generation in HG-induced H9c2 cells. H9c2 cells were incubated with NG (5.6 mM, NG group), NG plus mannitol (24.4 mM, M group), HG (30 mM, HG group), HG plus LV3 empty vector (HG + C group) or HG plus LV3 containing CD36 mutant (HG + KC group) for 72 h. (A) The TNF-α, IL-6 and IL-1β levels in the culture supernatant were measured by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. (B) The mRNA levels of TNF-α, IL-6 and IL-1β were measured by reverse transcription-quantitative PCR and normalized to β-actin. (C and D) CD36 in the nucleus and cytosol and nuclear translocation of NF-κB p65 protein were detected by western blotting. (C and E) IκBα protein in cytosolic extracts was measured by western blotting. (F) Immunofluorescence labeling with anti–NF-κB p65 (magnification, ×400). (G) Intracellular ROS were detected by flow cytometry. Data are expressed as the means ± SD. n=4. **P<0.01 vs. NG; #P<0.05 vs. HG. NF-κB, nuclear factor-κB; ROS, reactive oxygen species; HG, high glucose; NG, normal glucose; TNF, tumor necrosis factor; IL, interleukin.