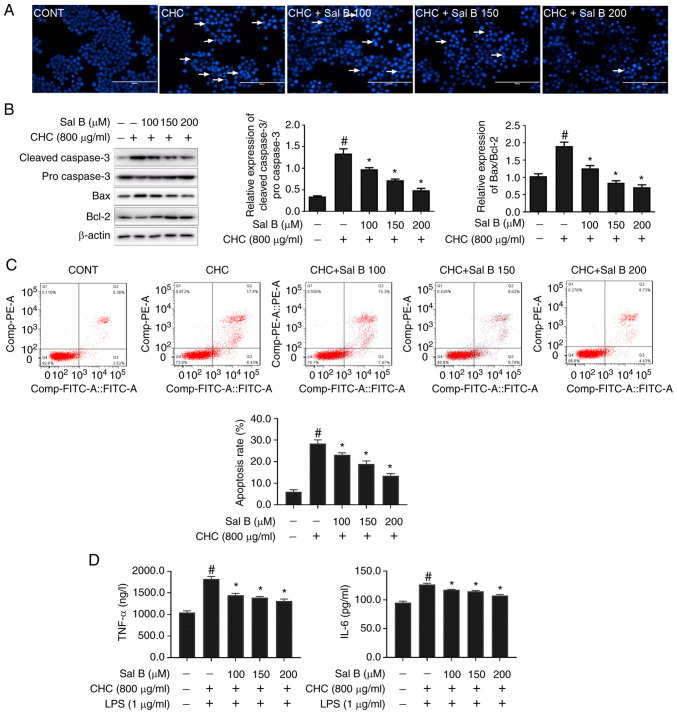
Figure 3.
Sal B attenuates CHC-induced apoptosis and the secretion of proinflammatory cytokines in RAW264.7 macrophages. The following groups are presented: CONT, untreated control; CHC, 800 µg/ml CHC; CHC + Sal B 100, 800 µg/ml CHC + 100 µM Sal B; CHC + Sal B 150, 800 µg/ml CHC + 150 µM Sal B; and CHC + Sal B 200, 800 µg/ml CHC + 200 µM Sal B. (A) Morphological features of CHC-induced and Sal B-treated RAW264.7 cells were evaluated by performing Hoechst 33258 staining. White arrows indicate apoptotic cells (scale bar, 100 µm). (B) Western blotting was performed to determine the expression levels of apoptosis-related proteins in CHC-induced RAW264.7 macrophages following treatment with Sal B (n=3). #P<0.05 vs. untreated control group; *P<0.05 vs. CHC group. (C) Annexin V-FITC/PI double staining was performed to assess the effect of Sal B on the apoptotic rate of CHC-induced RAW264.7 macrophages (n=3). (D) ELISAs were performed to assess the effect of Sal B on the release of TNF-α and IL-6 by CHC-induced RAW264.7 macrophages (n=3). #P<0.05 vs. untreated control; *P<0.05 vs. CHC. Sal B, salvianolic acid B; CHC, cholesterol crystal.