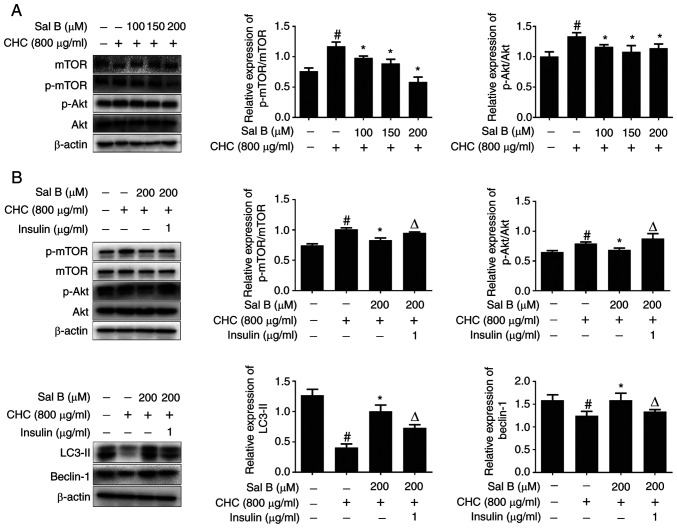
Figure 6.
Sal B improves CHC-induced autophagic dysfunction in RAW264.7 macrophages partially via inhibiting the Akt/mTOR signaling pathway. (A) Western blotting was performed to assess the effect of Sal B on the expression of Akt/mTOR signaling pathway-related proteins in RAW264.7 macrophages (n=3). The following groups are presented: CONT, untreated control; CHC, 800 µg/ml CHC; CHC + Sal B 100, 800 µg/ml CHC + 100 µM Sal B; CHC + Sal B 150, 800 µg/ml CHC + 150 µM Sal B; and CHC + Sal B 200, 800 µg/ml CHC + 200 µM Sal B. (B) Western blotting was performed to assess the effect of Sal B combined with insulin on the expression of Akt/mTOR signaling pathway- and autophagy-related proteins in CHC-induced RAW264.7 macrophages (n=3). The following groups are presented: CONT, untreated control; CHC, 800 µg/ml CHC; CHC + Sal B, 800 µg/ml CHC + 200 µM Sal B; and CHC + Sal B + insulin, 800 µg/ml CHC + 200 µM Sal B + 1 µg/ml insulin. #P<0.05 vs. untreated control; *P<0.05 vs. CHC; ΔP<0.05 vs. CHC + Sal B. Sal B, salvianolic acid B; CHC, cholesterol crystal; p, phosphorylated.