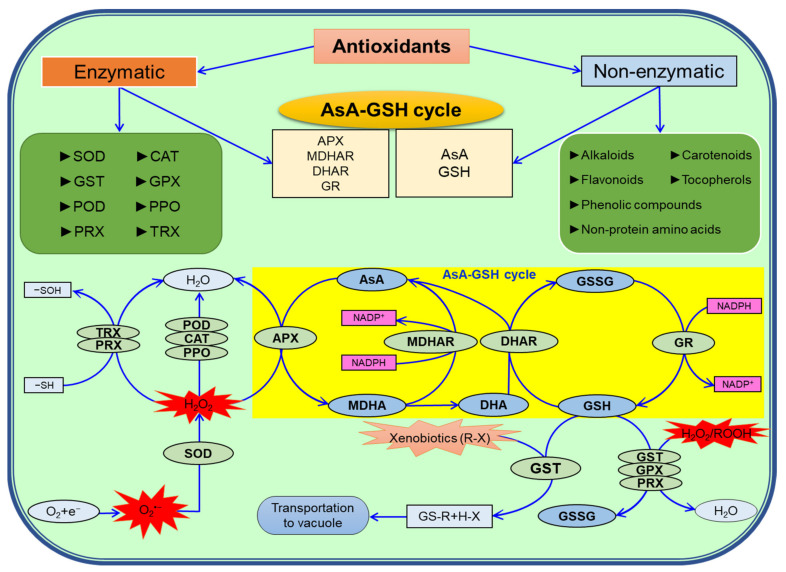
Figure 7.
Overview of different types of antioxidants and their combined mechanisms [2]. Detail descriptions are provided in the text. SOD—superoxide dismutase; CAT—catalase; POX—peroxidases; AsA—ascorbate; DHA—dehydroascorbate; GSSG—oxidized glutathione; GSH—reduced glutathione; APX—ascorbate peroxidase; MDHA—monodehydroascorbate; MDHAR—monodehydroascorbate reductase; DHAR—dehydroascorbate reductase; GR—glutathione reductase; GST—glutathione S-transferase; GPX—glutathione peroxidase; PPO—polyphenol oxidase; PRX—peroxiredoxins; TRX—thioredoxin; NADPH—nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate; O2—oxygen; e−—electrons; H2O2—hydrogen peroxide; O2•−—superoxide anion; R—aliphatic, aromatic or heterocyclic group; X—sulfate, nitrite or halide group; ROOH—hydroperoxides; -SH—thiolate; -SOH—sulfenic acid.