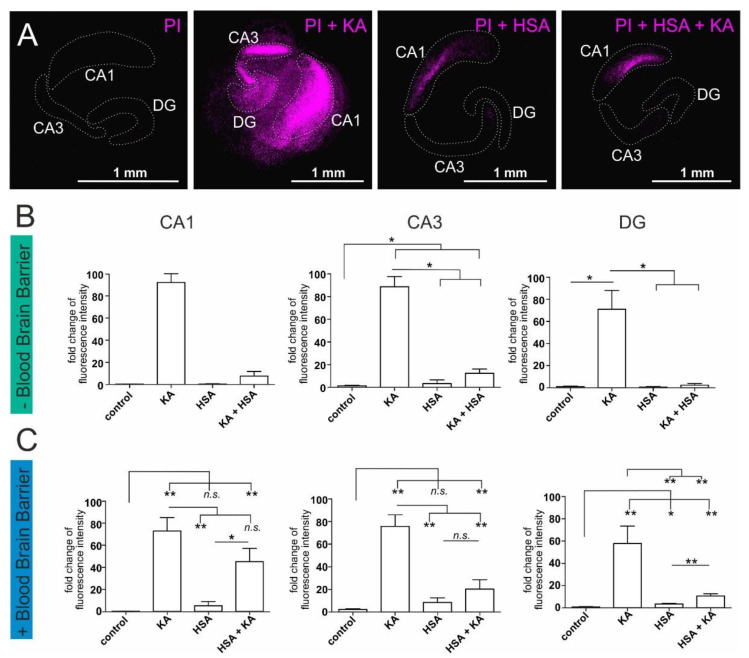
Figure 2.
Human serum albumin-mediated protection against excitatory stress applied on organotypic mouse hippocampus slice cultures. Treatment of hippocampal slice cultures with kainic acid (KA) results in cell death which can be measured by staining with propidium iodide (PI) (purple color). (A) Exemplary pictures of hippocampi in the respective treatment conditions with PI alone as untreated control, PI+KA, PI+ human serum albumin (HSA), and PI+KA+HSA. For better visibility, the fluorescence intensity of these exemplary pictures was amplified. The hippocampal regions are encircled with a dotted line. More unmodified exemplary pictures of PI-stained hippocampal slices can be found in the supplementary material (Supplemental Figure S1). (B) Cell death measurement in the cornu ammonis region 1 (CA1), the cornu ammonis region 3 (CA3), and the Dentate gyrus (DG) of hippocampal slice cultures without blood-brain barrier. (C) Cell death measurement in the CA1, the CA3, and the DG of hippocampal slice cultures on top of an artificial blood-brain barrier. Each experiment was performed using 3–4 biological replicates. PI: propidium iodide, KA: kainic acid, HSA: human serum albumin, CA1: cornu ammonis region 1, CA3: cornu ammonis region 3, DG: dentate gyrus. * p ≤ 0.05, ** p ≤ 0.01 was considered significant. n.s. not significant.