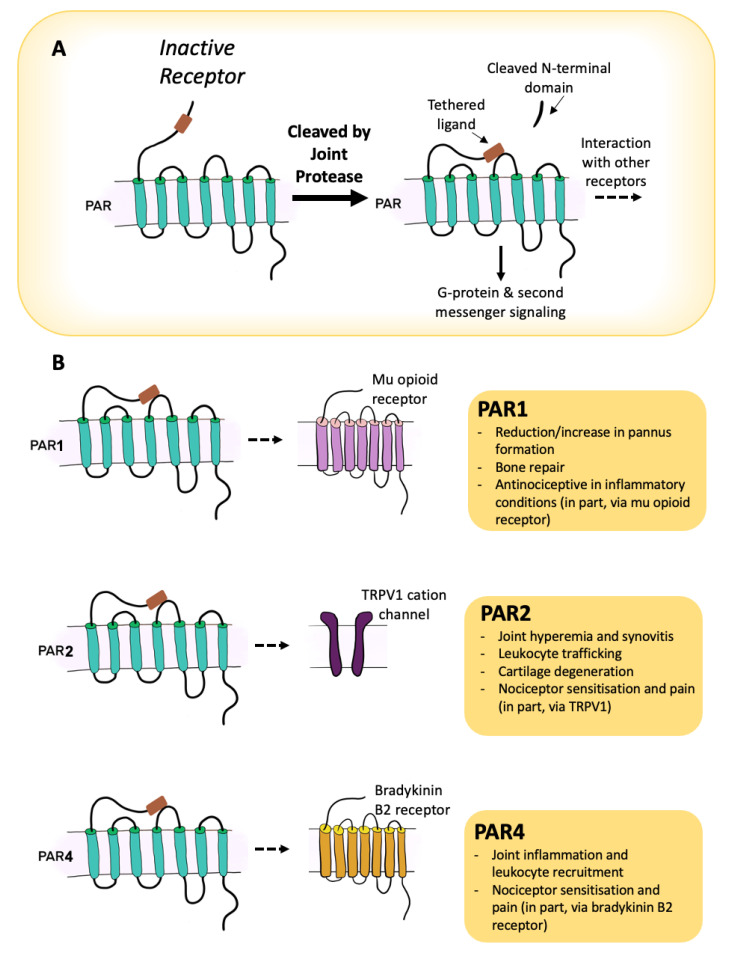
Figure 2.
Overview of the role of PARs in the control of joint inflammation and pain. Activation of a PAR is achieved by cleavage of the receptor with a proteolytic enzyme to reveal a tethered ligand that binds to the second extracellular loop, leading to G protein coupling and signalling (A). In joints, PAR-2 and -4 tend to be pro-inflammatory and pro-nociceptive, whereas PAR-1 has some protective properties (B).