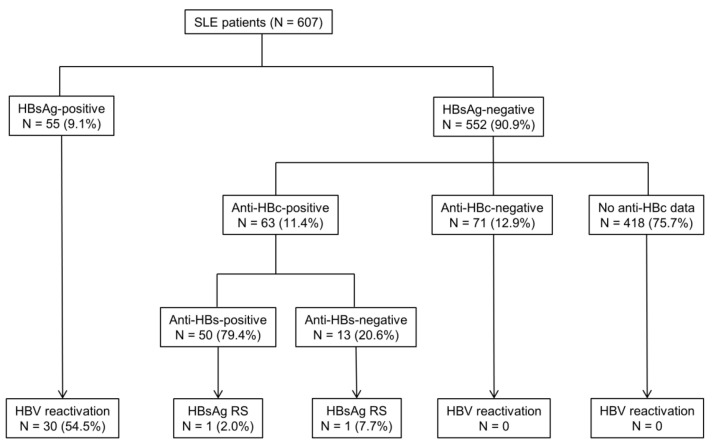
Figure 1.
HBV status and the incidence of hepatitis related to HBV reactivation in SLE patients. SLE patients were categorized according to hepatitis B surface antigen (HBsAg), antibody to hepatitis B core antigen (anti-HBc), and antibody to hepatitis B surface antigen (anti-HBs) status. HBV reactivation in HBsAg-positive patients was defined as either an increase in HBV DNA > 1 Log10 IU/mL compared with baseline or HBV DNA > 20,000 IU/mL in cases without baseline HBV viral load after diagnosis or the use of immunosuppressive agents. HBsAg reverse seroconversion (RS) in HBsAg-negative/antibody to hepatitis B core antigen-positive patients was defined as reappearance of HBsAg in the serum.