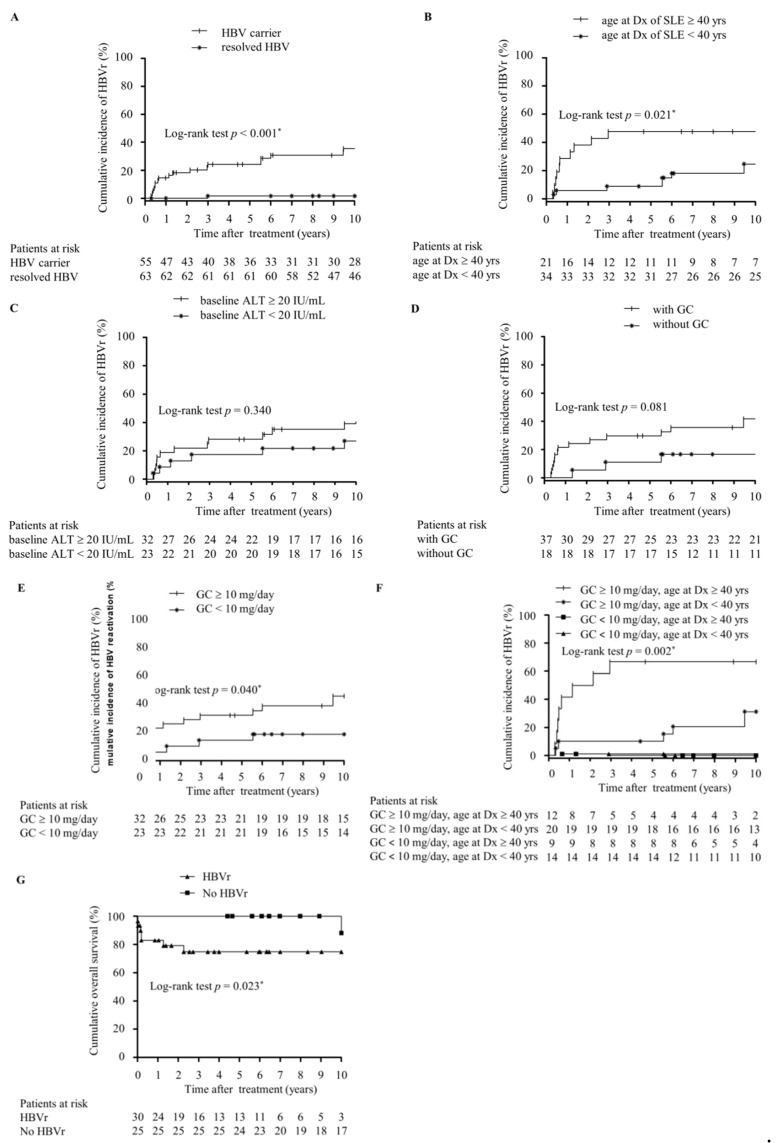
Figure 2.
Cumulative incidence of hepatitis and HBV reactivation in SLE patients and outcome of HBsAg-positive SLE patients. (A) 10-year (yr) cumulative incidence of hepatitis related to HBV reactivation (HBVr) in HBsAg-positive and resolved hepatitis B SLE patients after treatment with immunosuppressive therapy. (B–E) 10-yr cumulative risk of HBVr in HBsAg-positive SLE patients stratified by the age at diagnosis (Dx) of SLE (older or younger than 40 years) (B), stratified by baseline serum ALT (more or less than 20 IU/mL) (C), stratified by with or without glucocorticoid(GC)-containing immunosuppressive therapy (D), stratified by with or without GC ≥ 10 mg/day prednisolone equivalents (E), and stratified by the age at Dx of SLE (older than 40 years with GC ≥ 10 mg/day prednisolone equivalents or not) (F). (G) 10-yr survival in 55 HBsAg-positive SLE patients with and without HBVr. The duration of follow-up was calculated from the time of treatment for SLE to the date of the last visit or death. The incidence of HBVr or mortality was evaluated by Kaplan–Meier analysis and log-rank test. p value < 0.05 was considered statistically significant.