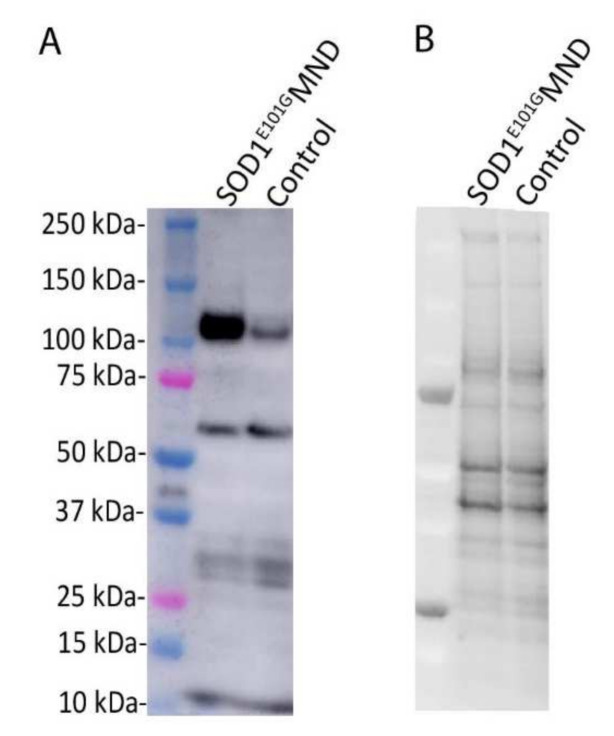
Figure 1.
(A) Relative levels of EphA4 (110 kDa) are 5× higher in iPSC-derived motor neurons from a SOD1E101G MND patient compared to iPSC-derived motor neurons from a healthy control. (B) Corresponding total protein blot from the SOD1E101G MND patient and healthy control. Four-week-old iPSC-derived motor neurons were harvested by rinsing in 1× PBS followed by manual scraping in RIPA buffer (50mM Tris-HCl pH 7.4, 1% NP40, 0.25% Na-deoxycholate, 150 Mm NaCl, 1mM EDTA, phosphate (PhosSTOP, Roche) and protease (complete protease inhibitor cocktail, Roche) inhibitors). Cellular debris was pelleted by means of centrifugation at 10,000× g for 10 min at 4 °C. The cleared protein lysate was quantified via BCA and 20 µg of protein was used for Western blotting. Proteins were denatured by boiling at 95 °C for 5 min in Laemmli buffer with 5% β-mercaptoethanol and loaded on a Criterion 4–20% stain-free gel (Biorad). Samples were electrophoresed in SDS-PAGE buffer and transferred onto a PVDF membrane. The membrane was imaged using the Criterion stain-free gel imaging system (Biorad) to obtain total protein values for quantification. The membrane was blocked in 5% skim milk in TBS for 1 h and incubated in EphA4 antibody (1:1000 in 5% skim milk in Tris-buffered saline solution, mouse anti-EphA4, ECM Bioscience) overnight at 4 °C. The membrane was then incubated in an HRP-conjugated secondary antibody and EphA4 (approximate molecular weight 110 kDa) was detected using Pierce ECL Plus Western Blotting substrate (Thermo Fischer) and the chemiluminescence function on the Amersham GE 600 Imager (GE Life Sciences). Densitometry analysis was conducted using Image Studio Lite version 5.2 and each sample measurement was normalised to its corresponding total protein value.