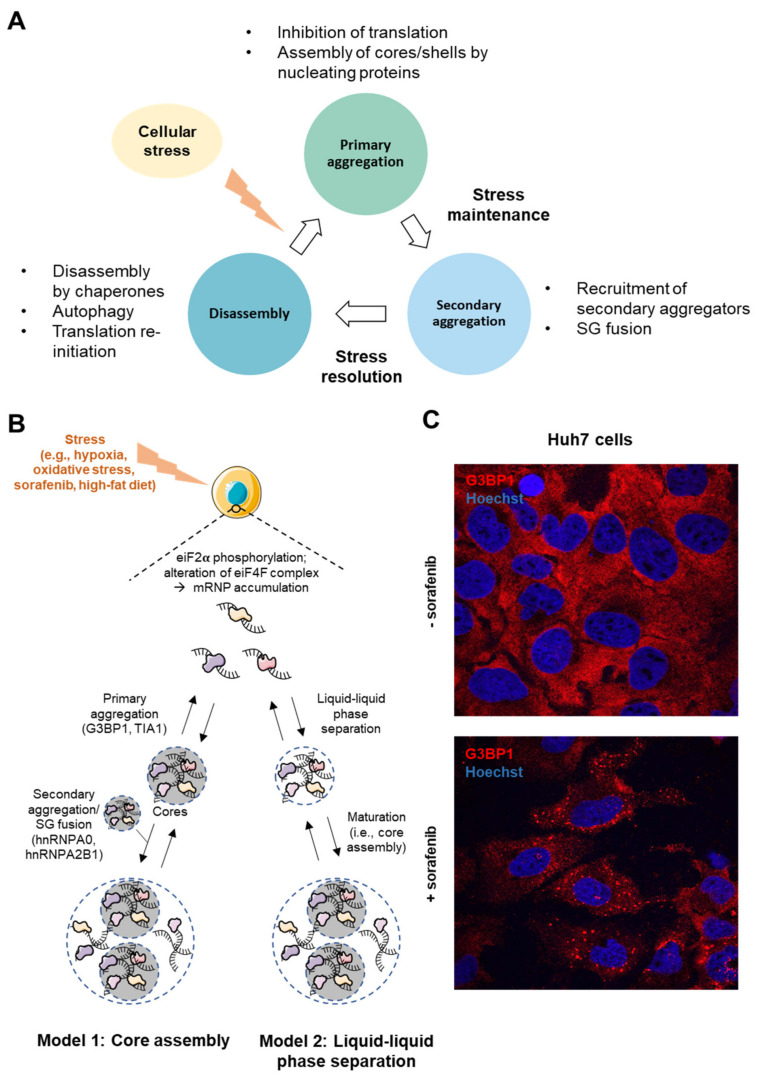
Figure 2.
Stress Granule assembly. (A) The cycle of stress granule formation and disassembly. (B) SGs in the liver can form during stressful events such as hypoxia, oxidative stress, sorafenib treatment or high-fat diet. Two models of SG assembly have been described. In the “core first” model, nucleating proteins (e.g., G3BP1 and TIA1) form a stable core, and later, other SG-associated proteins are recruited to form the dynamic shell. Alternatively, in the ‘LLPS first’ model, proteins bound to transcripts assemble through interactions of their IDD domains. Further on, highly dense fractions form SG cores. (C) Confocal microscopy images of SG formation (G3BP1 staining in red; Hoechst-33342 staining in blue) in hepatic Huh7 cancer cells after 24 h treatment with 5 μM sorafenib (63× magnification).