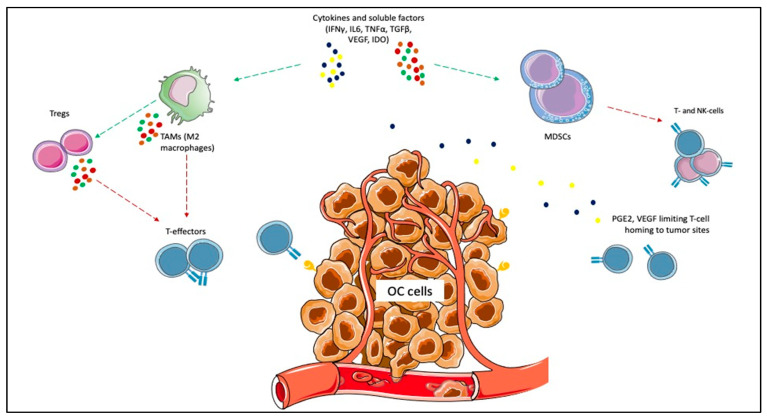
Figure 1.
Immunosuppressive elements of ovarian cancer (OC) microenvironment. Cytokines and other soluble factors, such as interferon-gamma (IFNγ), tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNFα), interleukin (IL)-6, IL-10, and transforming growth factor-beta (TGFβ) induce the proliferation of myeloid-derived suppressor cells (MDSCs) and the polarization of tumor-associated macrophages (TAMs) towards the M2 subtype. MDSCs exert immunosuppressive functions, such as the inhibition of T-effector and natural killer (NK)-cells. The inflammatory cytokines cooperate to induce cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) and lead to prostaglandin E2 (PGE2) synthesis, which limits T-cell recruiting at tumor sites. M2 macrophages promote immunosuppression by producing cytokines (e.g., IL-1R, IL-10, C-C Motif Chemokine Ligand [CCL]17, CCL20, CCL22) that inhibit T-effectors proliferation and enhance Tregs function.