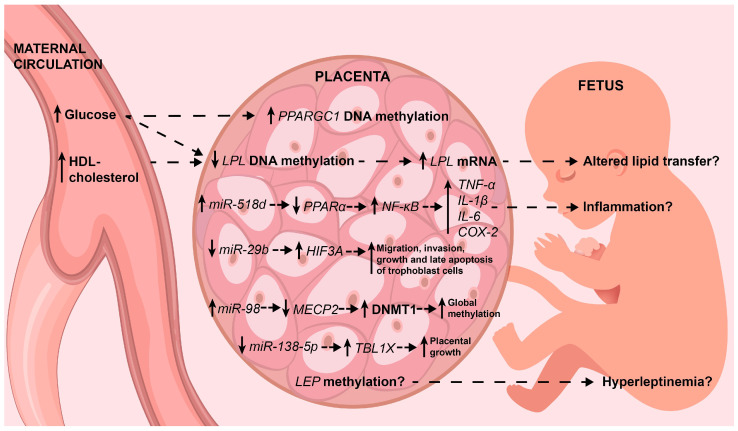
Figure 1.
The main placental epigenetic alterations associated with GDM. Epigenetic alterations and their effects on target genes are shown (see the text for deeper details). Interestingly, some explain, in part, the well-known pro-inflammatory status and excessive growth of the placenta. On tissue, solid arrows indicate up-regulation or down-regulation in maternal circulation and the fetus indicate low or high circulating levels. Dotted line arrows indicate association. HDL-cholesterol: high-density lipoprotein cholesterol; mRNA: messenger ribonucleic acid; FFA: free fatty acids; PPARα: proliferator-activated receptor alpha; NF-κB: nuclear factor-kappa B; TNF-α: tumoral necrosis factor alpha; IL-1β: interleukin 1 beta; IL-6: interleukin 6; COX-2: cytochrome C oxidase subunit II; HIF3A: hypoxia inducible factors 3A; MECP2: methyl CpG binding protein 2; DNMT1, DNA methyltransferase 1; TBL1X: transducin β–like protein 1; LEP: leptin.